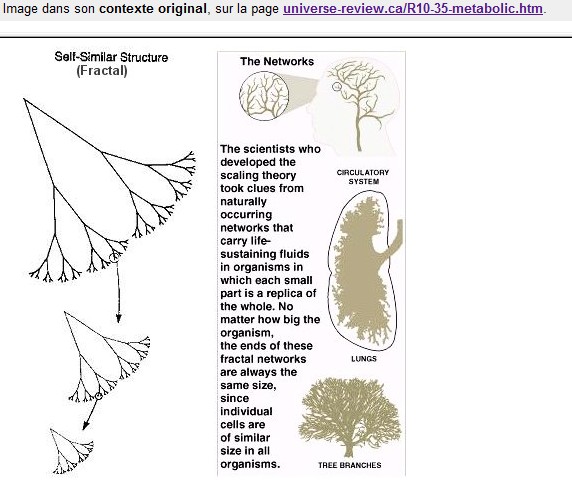
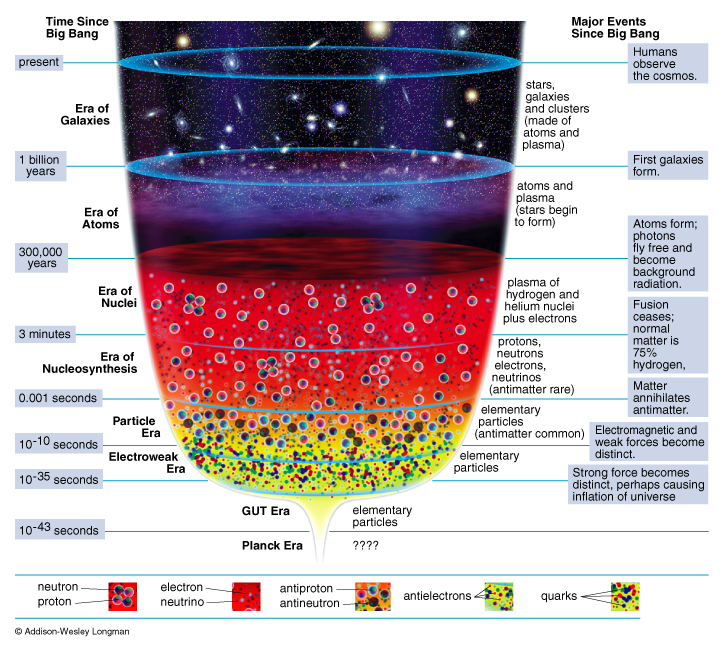
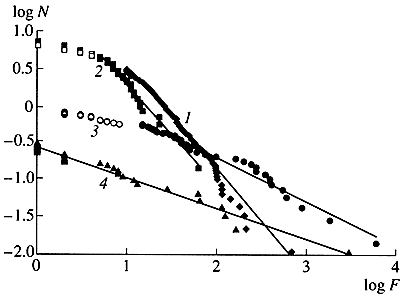
Pareto-Zipf-Mandelbrot (parabolic fractal) distributions are observed in virtually all fields of research
covering the evolution from the big bang over the evolution of man
 to the world wide
web.
to the world wide
web. contact: winiwarter@bordalierinstitute.com
contact: winiwarter@bordalierinstitute.com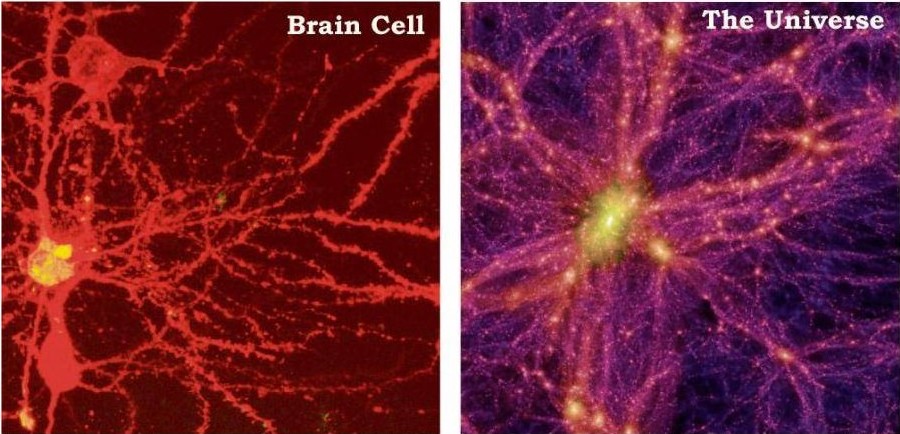
| “ | That theory, as it is expressed by the maximum power principle, addresses the empirical question of why systems of any type or size organize themselves into the patterns observed. Such a question assumes that physical laws govern system function. It does not assume, for example, that the system comprising economic production is driven by consumers; rather that the whole cycle of production-consumption is structured and driven by physical laws. |
 to the world wide
web.
to the world wide
web.
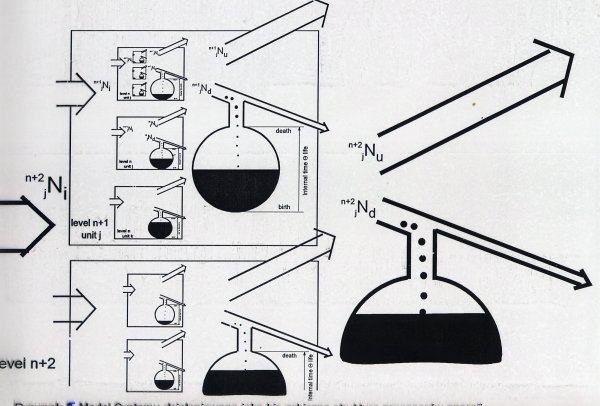
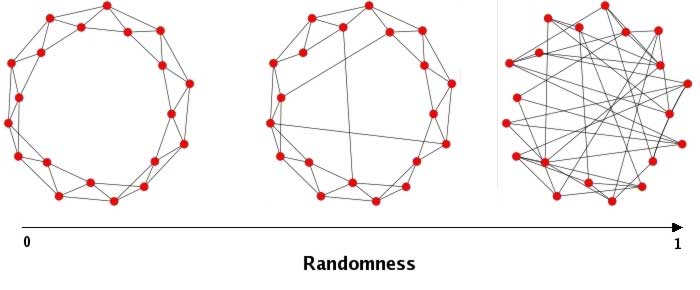
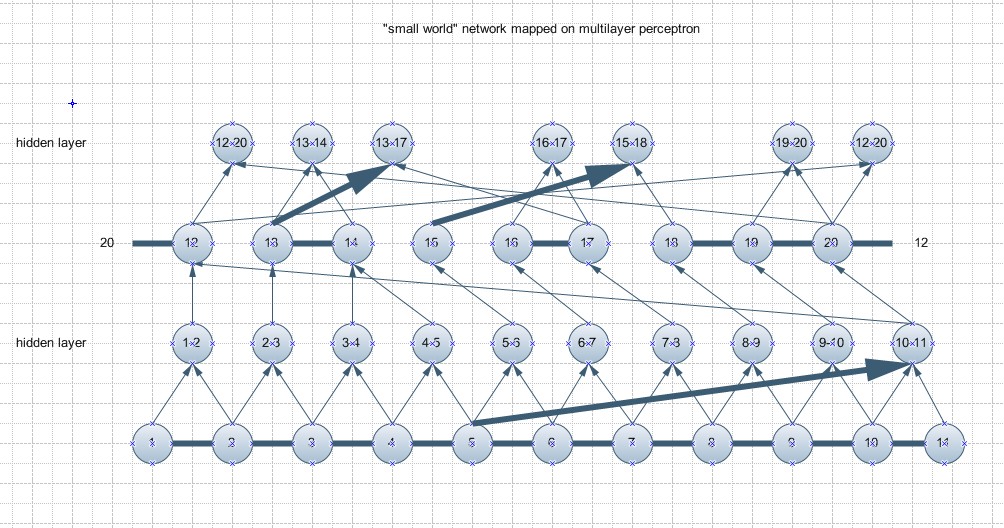
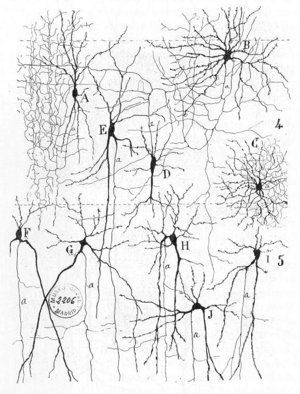
 Hebb's rule "cells
that fire together, wire together"
Hebb's rule "cells
that fire together, wire together"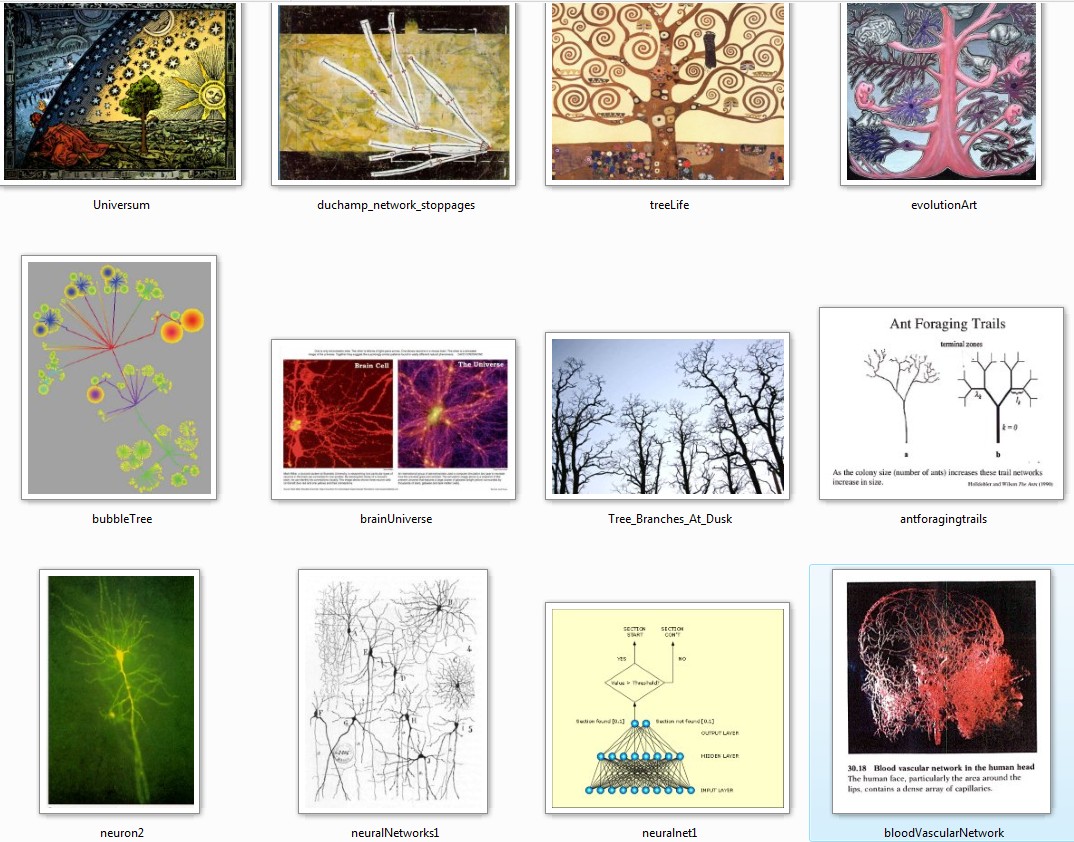
 to the world wide
web.
to the world wide
web.





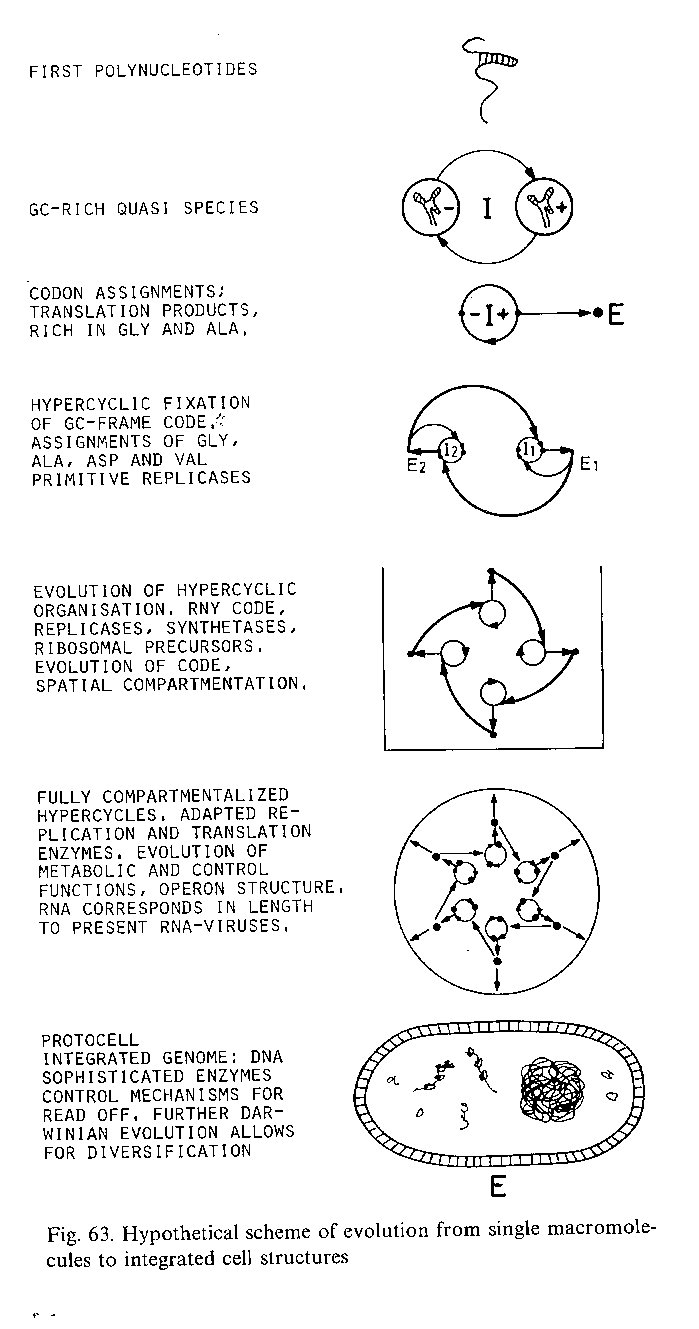
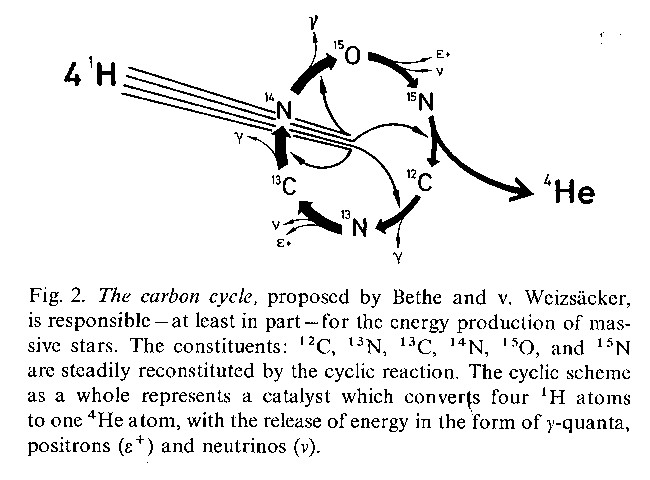 {Eigen & Schuster
1979:3}
{Eigen & Schuster
1979:3}
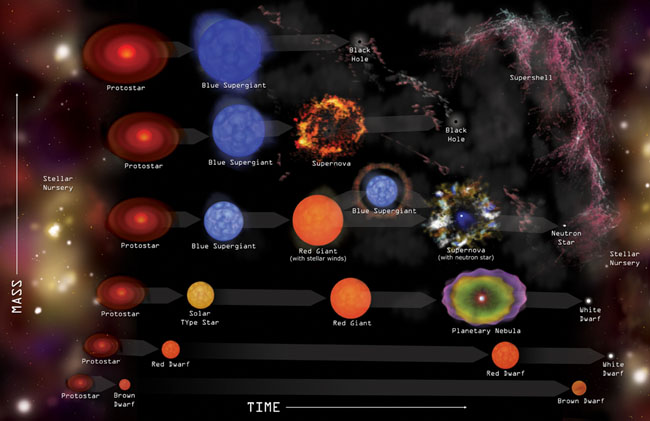









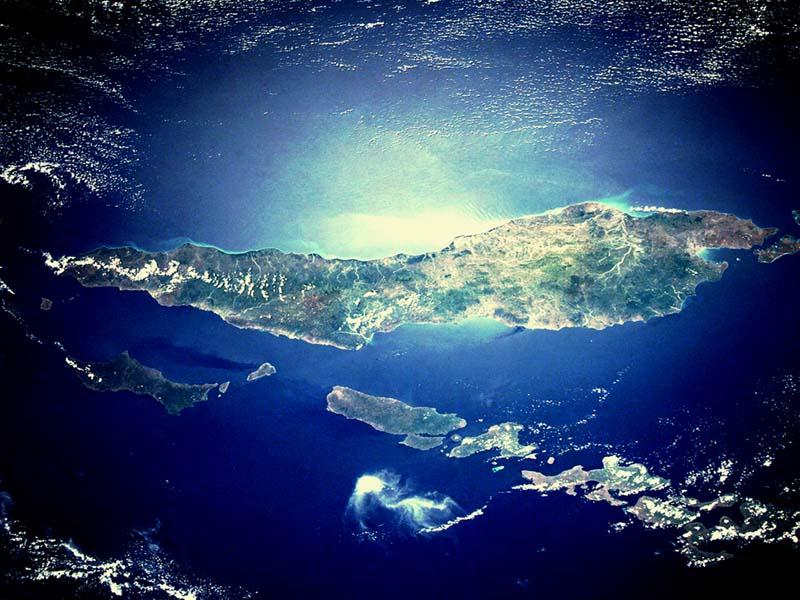
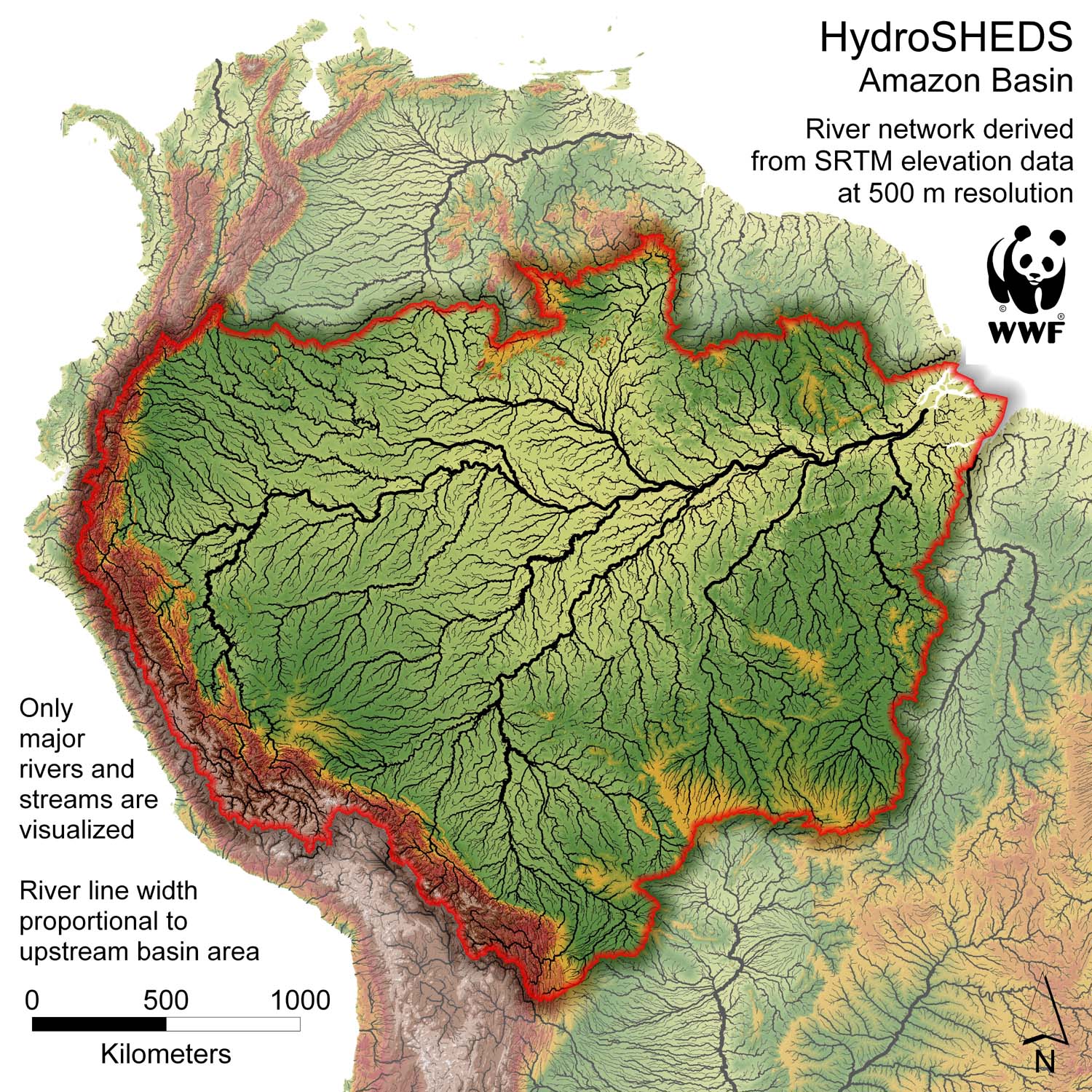

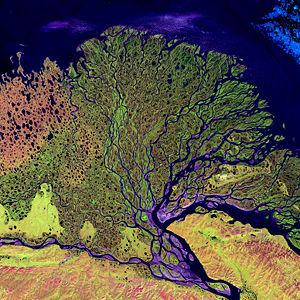

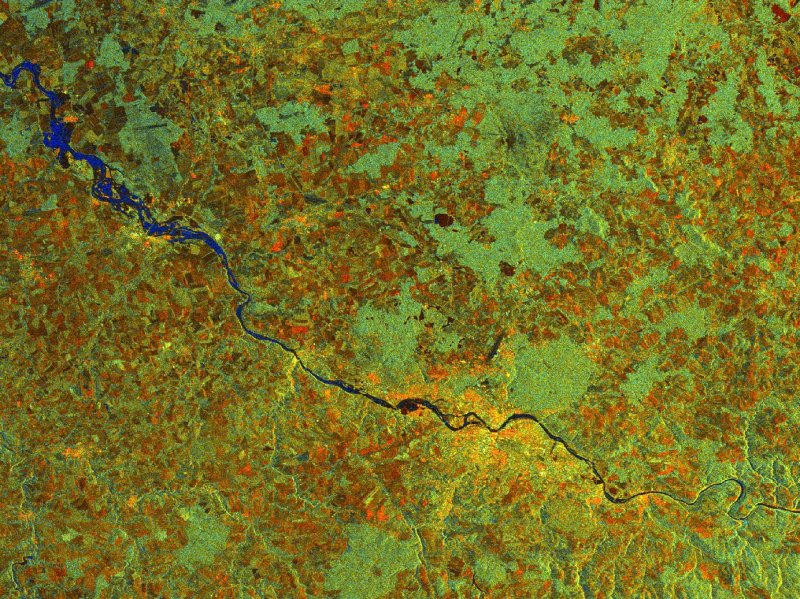





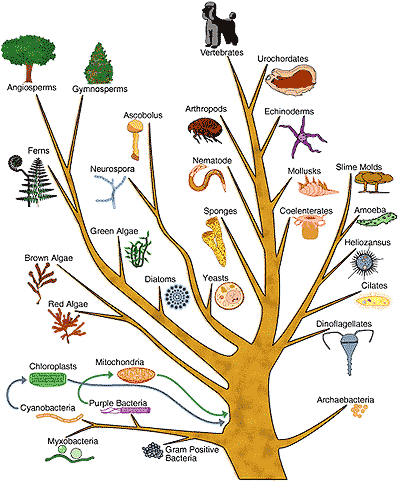
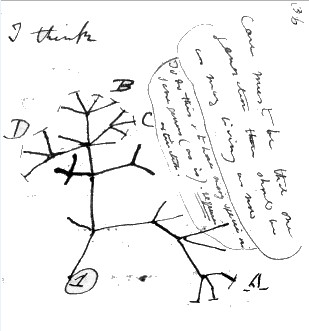 Darwin Tree of Life
Darwin Tree of Life



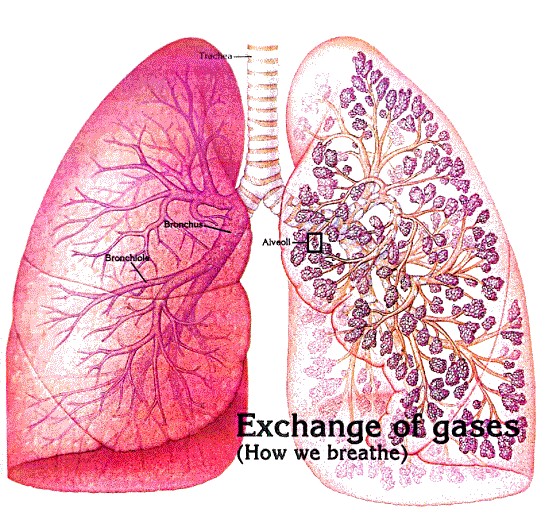
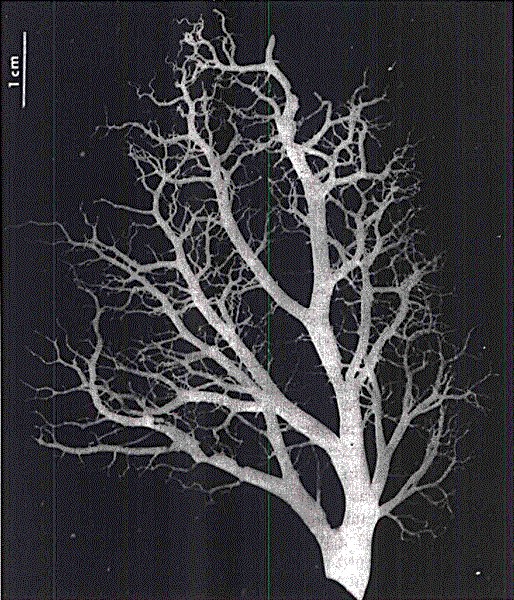 bloodvessel
bloodvessel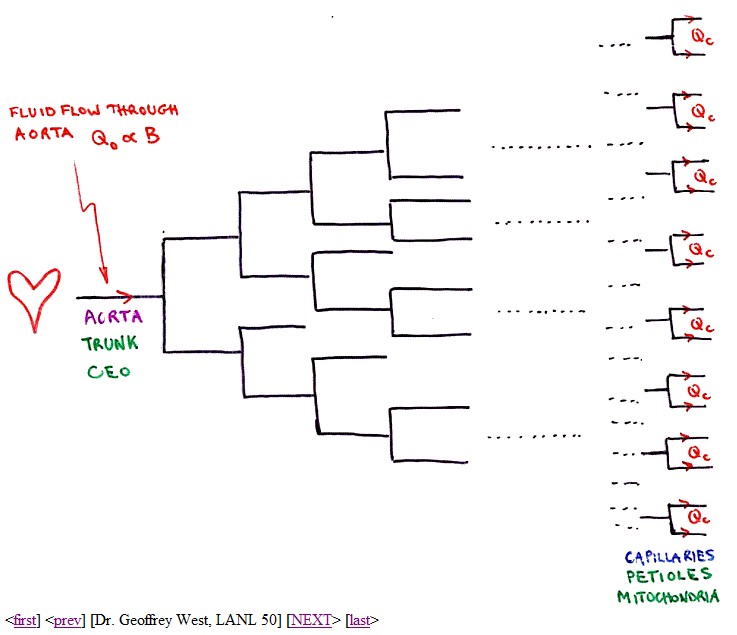



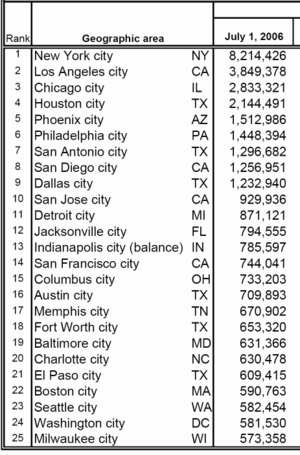
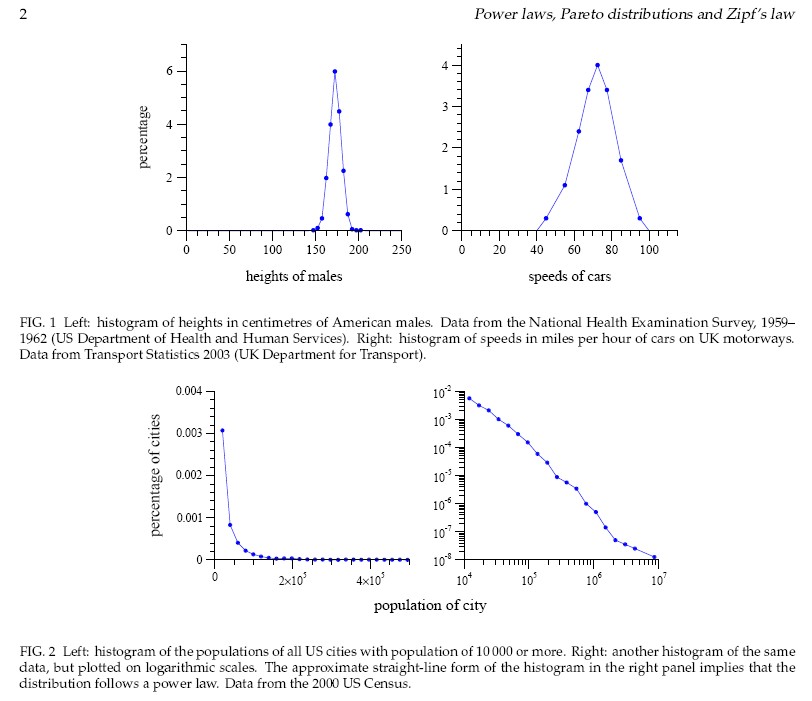
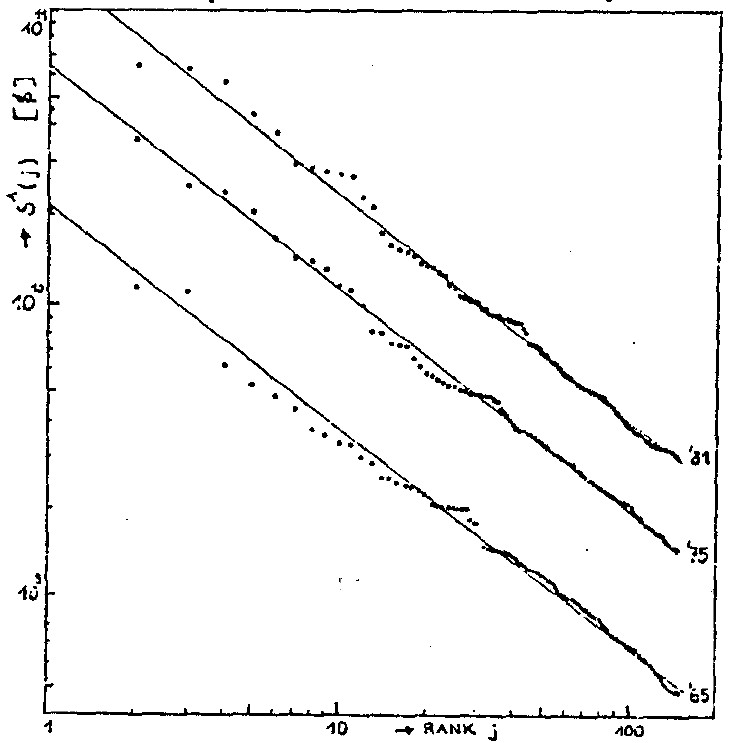
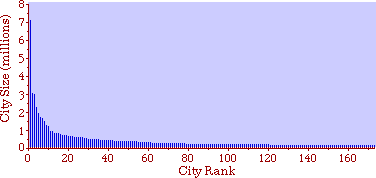 largest US cities in ordinary
scale (straight line in log-log scale)
largest US cities in ordinary
scale (straight line in log-log scale)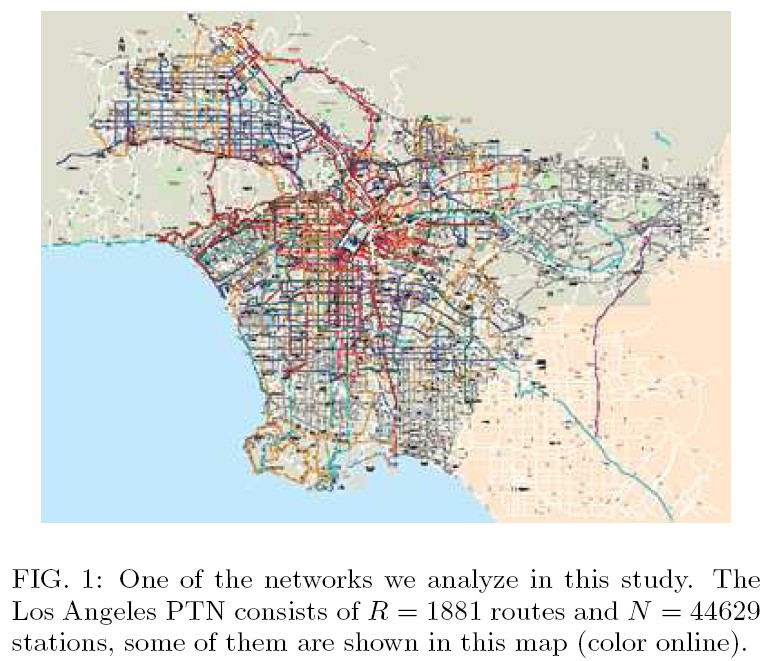 "Marguerite
Youcenar" monumental sculpture of elsa genese
"Marguerite
Youcenar" monumental sculpture of elsa genese "Marguerite
Youcenar" monumental sculpture of elsa genese
"Marguerite
Youcenar" monumental sculpture of elsa genese
 "Marguerite
Youcenar" monumental sculpture of elsa genese
"Marguerite
Youcenar" monumental sculpture of elsa genese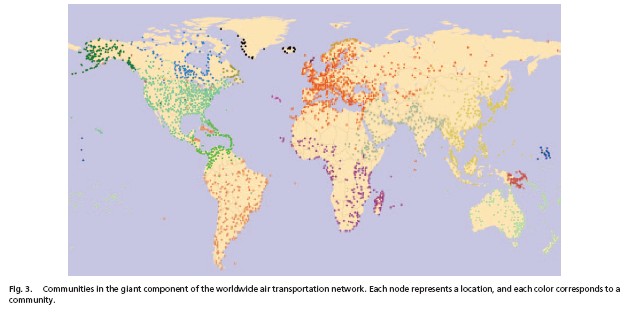
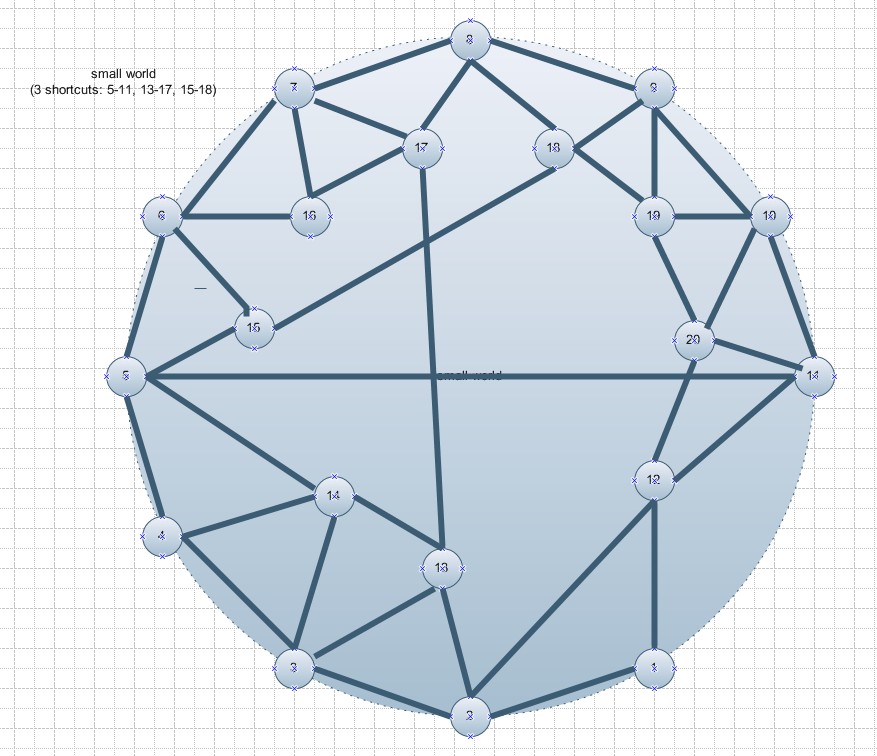
 The world-wide
airport network
is a small-world
The world-wide
airport network
is a small-world






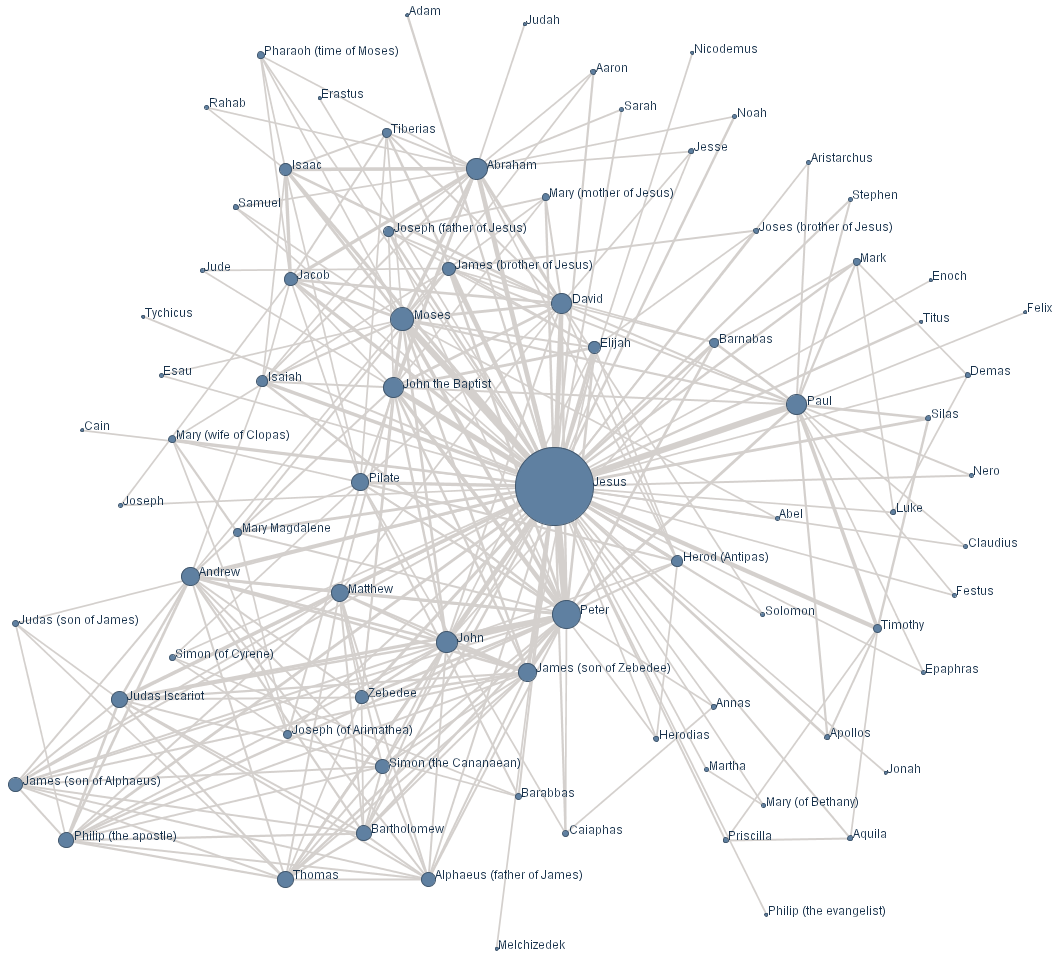
 size
distribution of religous
groups are of the PZM
Pareto-Zipf-Mandelbrot type (parabolic fractal)
size
distribution of religous
groups are of the PZM
Pareto-Zipf-Mandelbrot type (parabolic fractal)


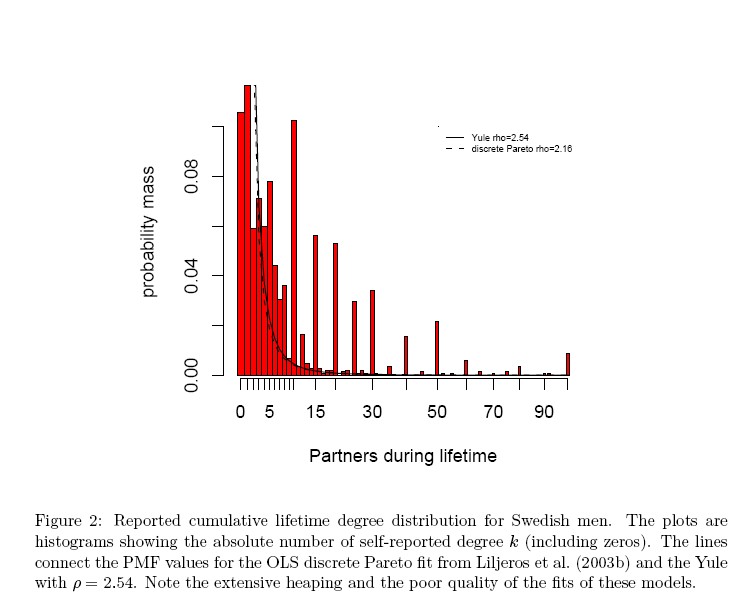



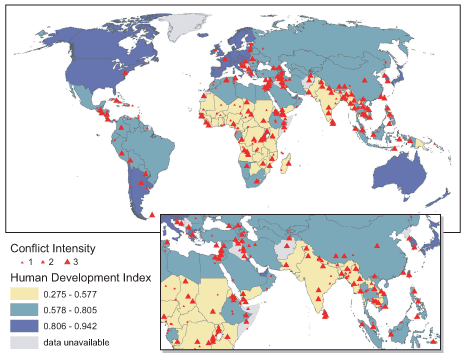


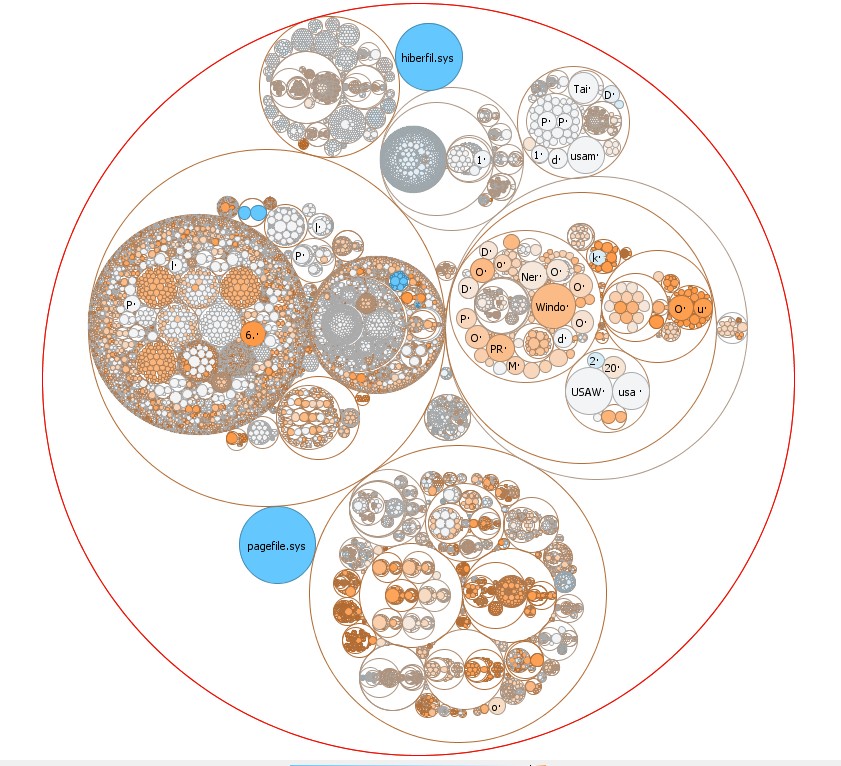
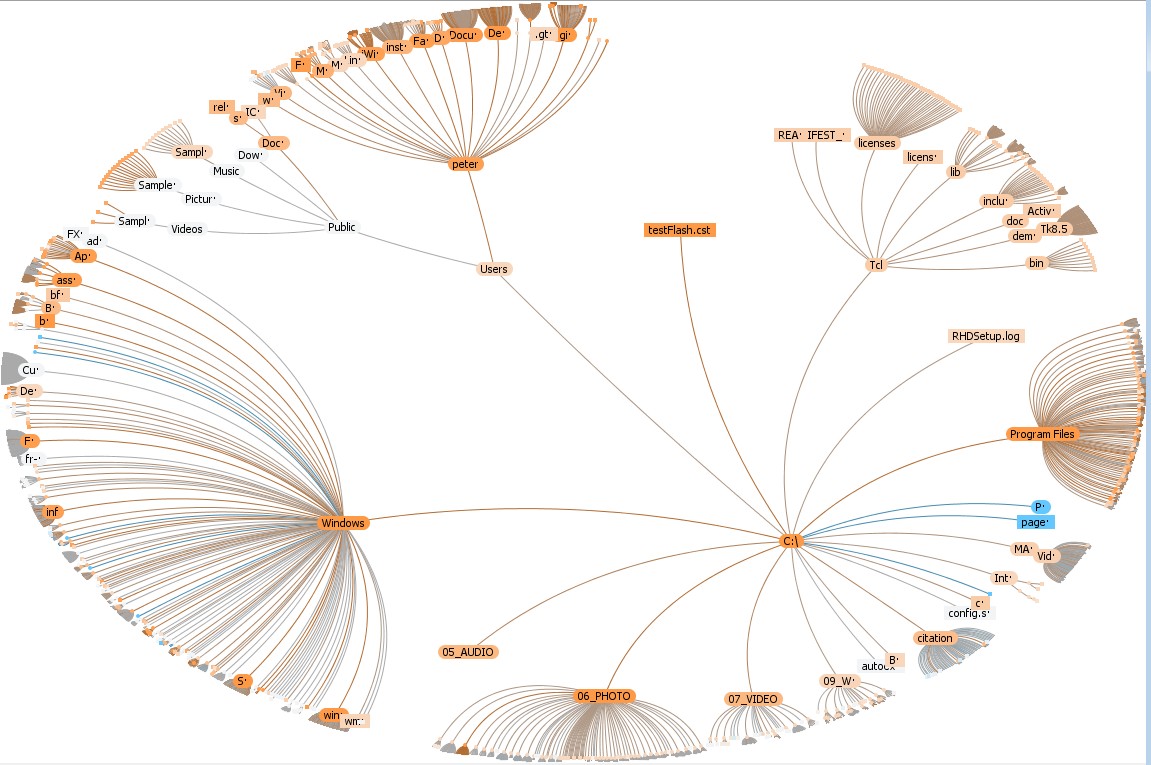
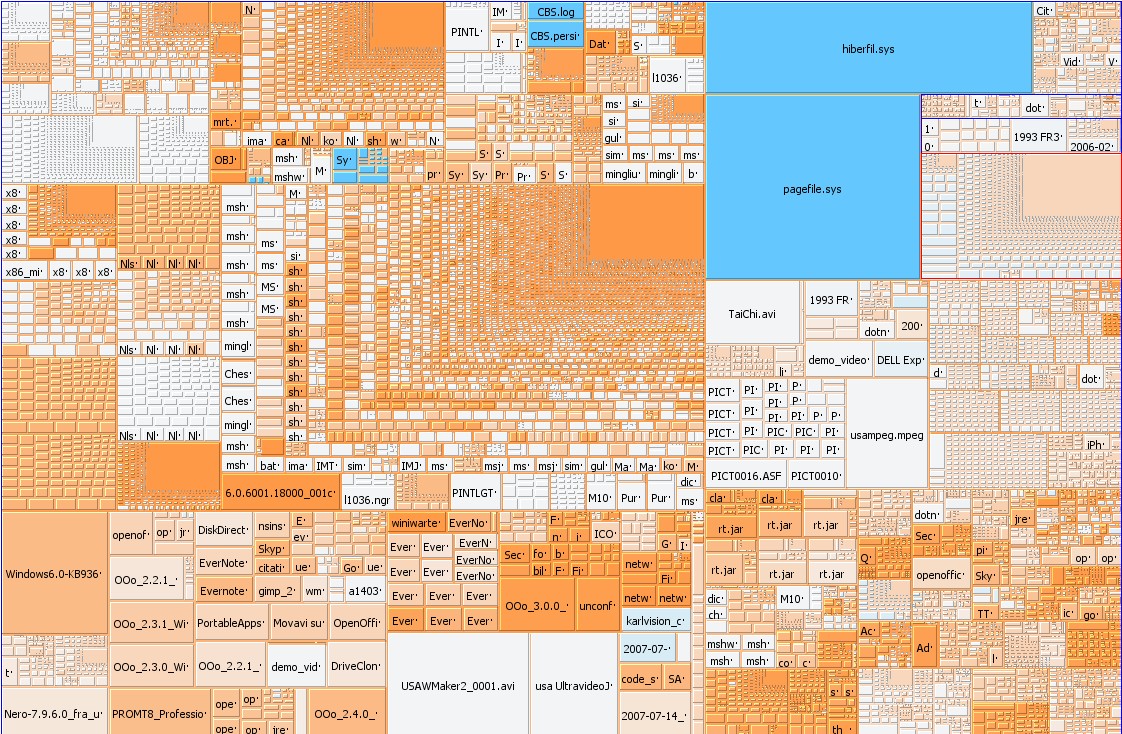
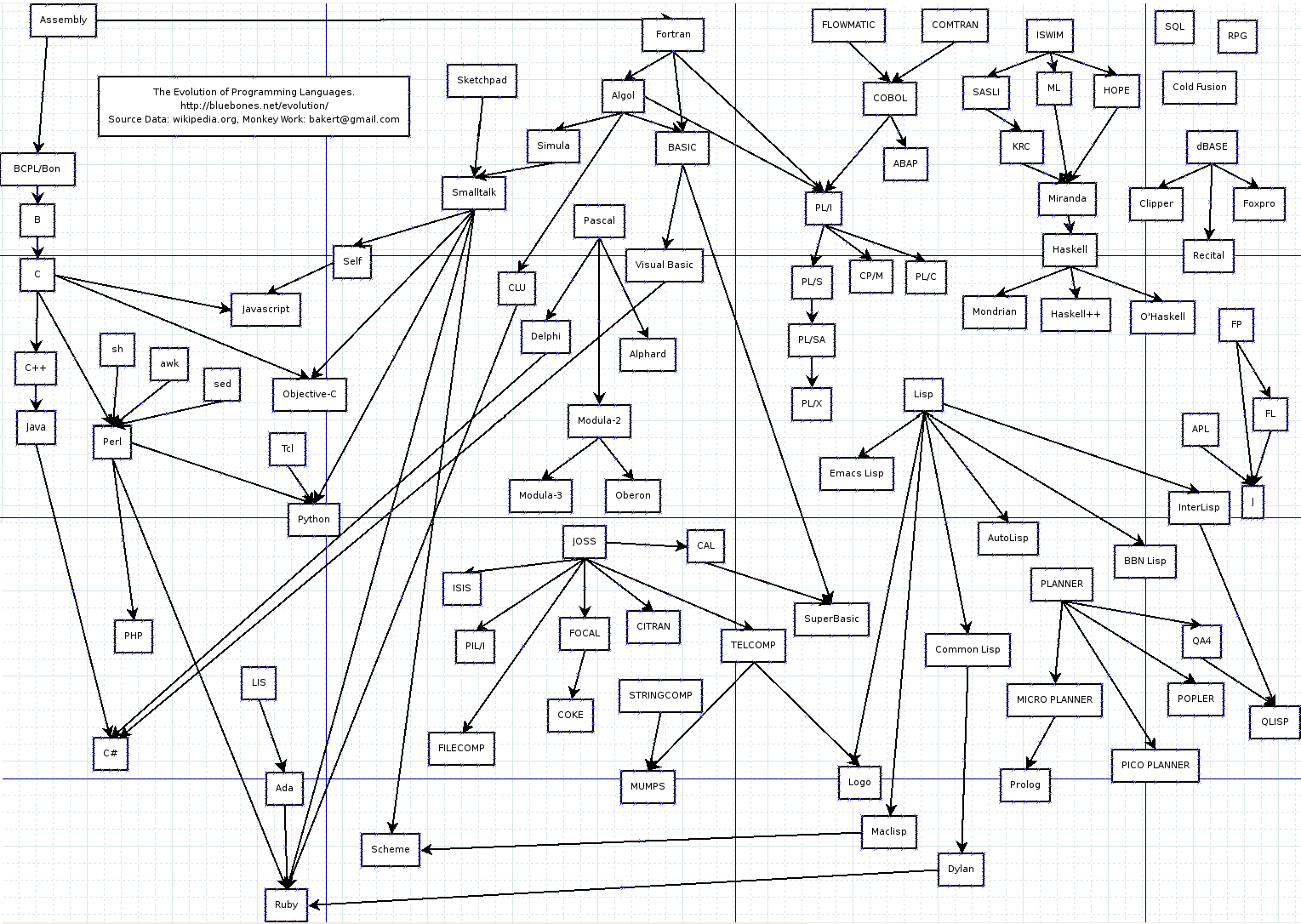




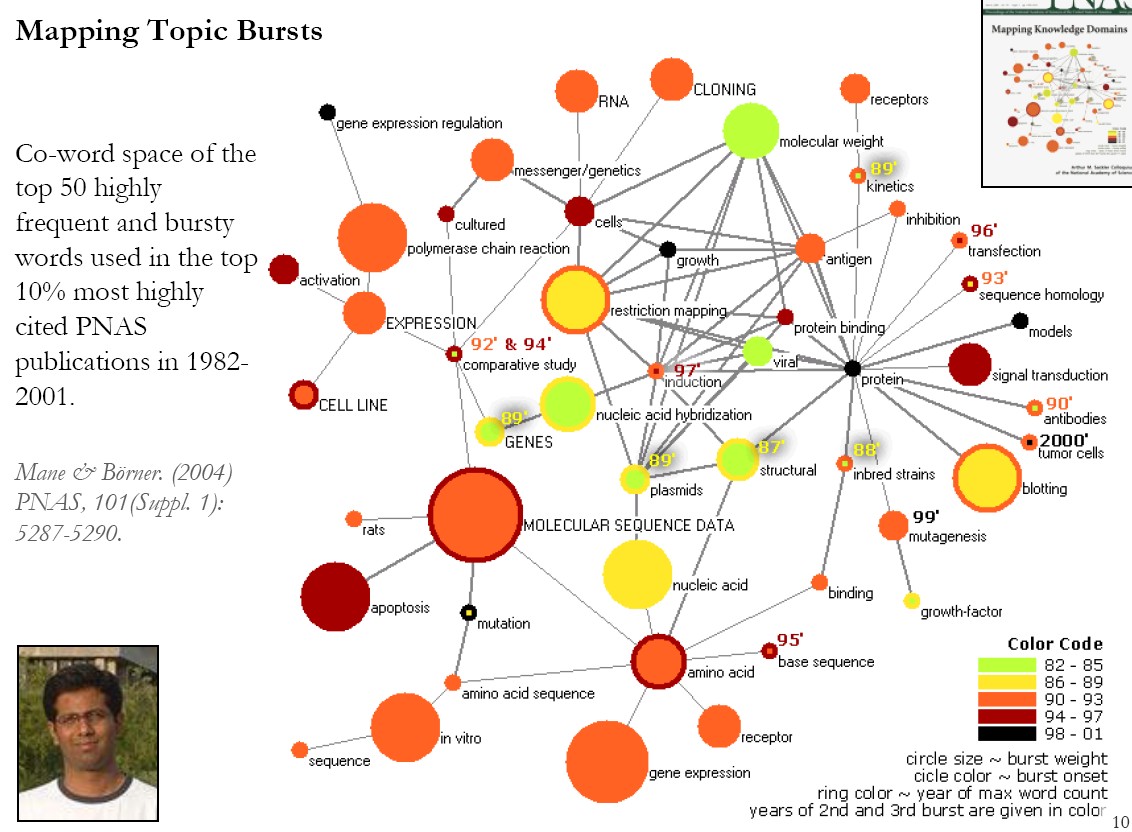
|
Therefore, SEIR simulates infectious
diseases at the collective level by .....
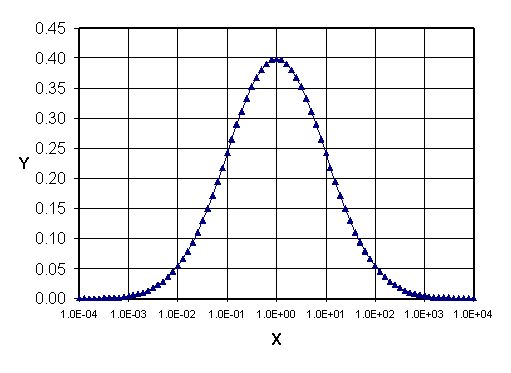
the relative frequency in the use of words in language (Zipf's
law) or the ..
|

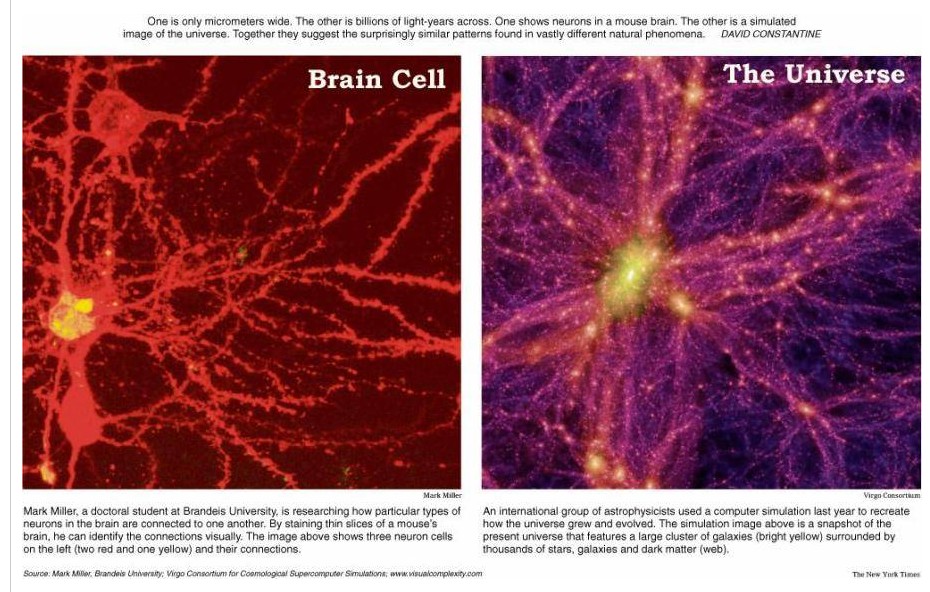

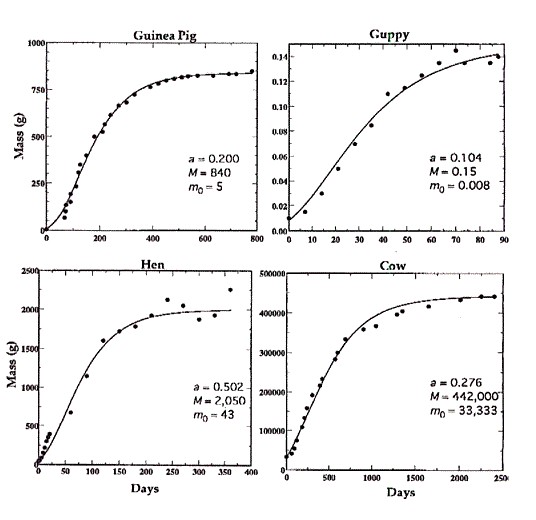
"We are all agreed that your theory is crazy. The question which divides us is whether it is crazy enough to have a chance of being correct. My own feeling is that is not crazy enough. "
Niels Bohr on Pauli's theory of elementary particles
from Arne A. Wyller's The Planetary MindNiels Bohr on Pauli's theory of elementary particles
from Arne A. Wyller's The Planetary MindNiels Bohr on Pauli's theory of elementary particles
from Arne A. Wyller's The Planetary Mind.
| “ | That theory, as it is expressed by the maximum power principle, addresses the empirical question of why systems of any type or size organize themselves into the patterns observed. Such a question assumes that physical laws govern system function. It does not assume, for example, that the system comprising economic production is driven by consumers; rather that the whole cycle of production-consumption is structured and driven by physical laws. |
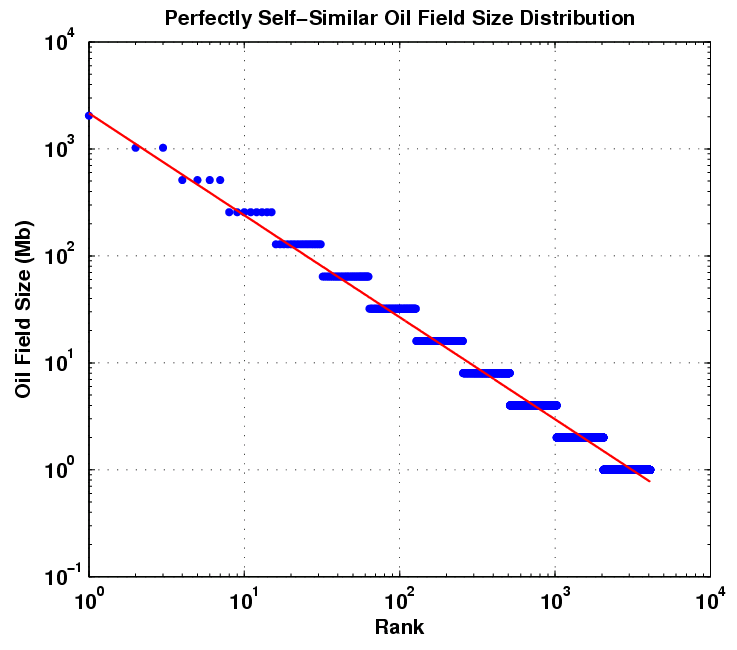
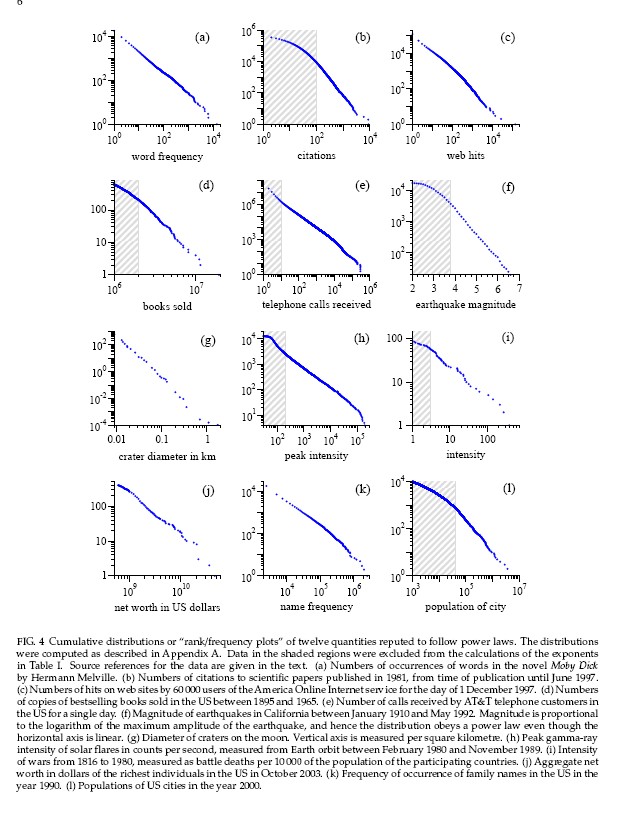
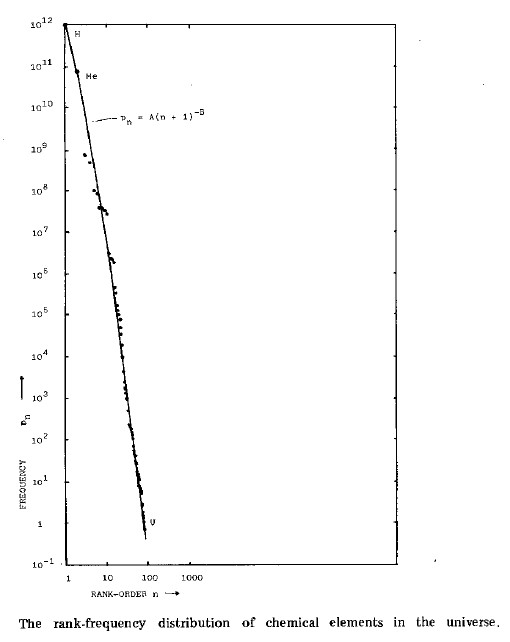
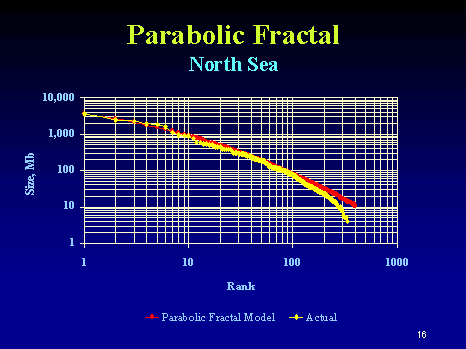
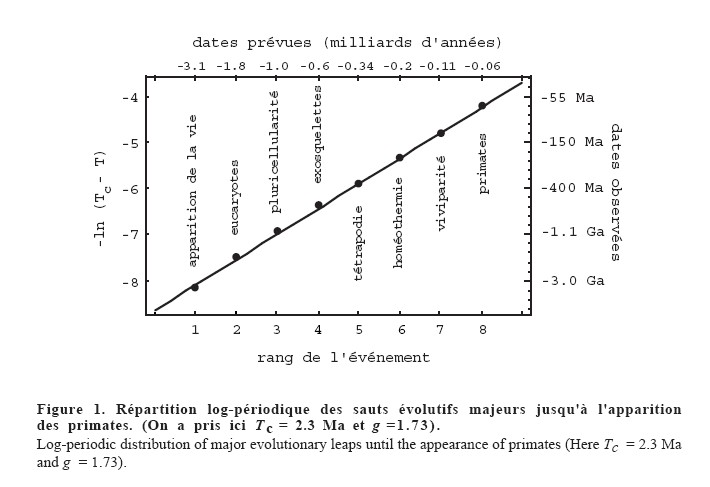
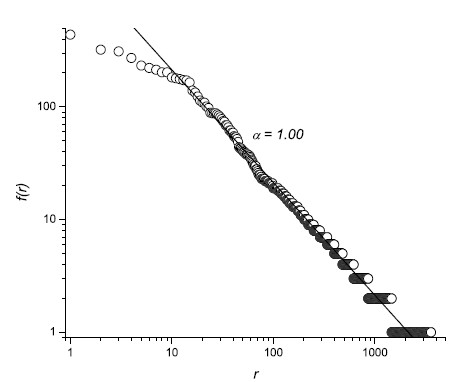
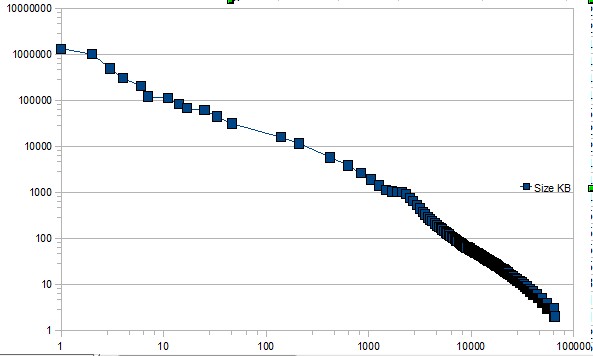
| For
income distributions, city-size distributions and word frequencies we
observe long-tailed distribution power laws of the
PARETO-ZIPF-MANDELBROT (parabolic fractal) type. In fact on all levels of evolution from the big bang to the world wide web - for properties of units belonging to the same astrophysical, geological, biological, ecological, urban, social, linguistic, economic, mechanical machinery or computer system - we observe similar regularities referred to as Pareto law, Zipfs law or rank-size law. We give a short historical overview over the discovery of these empirical regularities. Then we review a variety of theoretical tentatives, none of which can  explain explain that similar regularities are observed in such
an incredible wide range of scientific research areas. that similar regularities are observed in such
an incredible wide range of scientific research areas. |
| Finally,
departing from a very specific model - describing tribo-vibro-acoustic
processes in machines - we propose a generalized theoretical framework
in terms of energy transformation with
limited internal energy
dissipation capacity, which is applicable to
all fields. |
The proposed model  unifies unifies a large variety of concepts and applies a coherent terminology to
fields, which have at first sight nothing in common.
a large variety of concepts and applies a coherent terminology to
fields, which have at first sight nothing in common.For the observed generalized life symptoms, theoretical predictions can be compared with past and future empirical observations. |
| What is most important is the model's inference power: from the observations of a set of units at a given moment of life-time (a snapshot of the system), one can predict the average behaviour of a single unit over its entire life-time. |
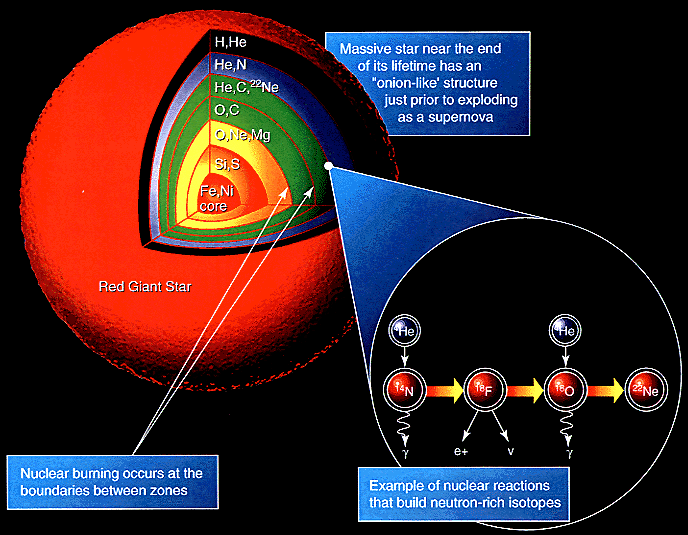
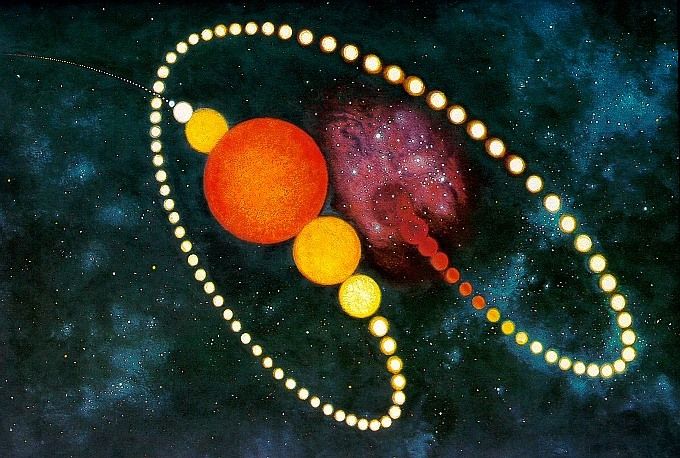
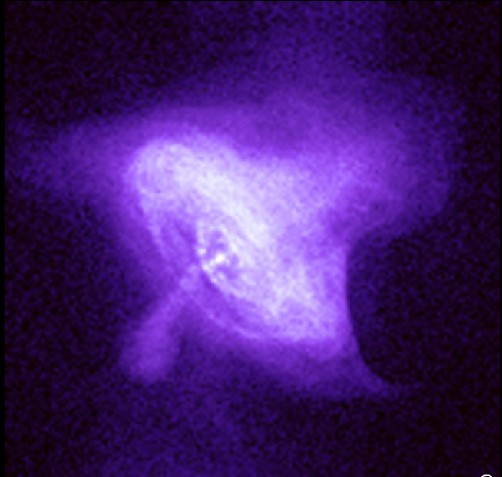
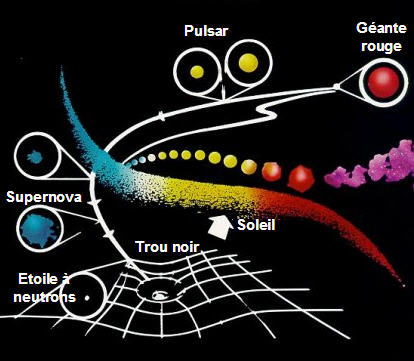 birth and death of star
birth and death of star
 Hebb's rule "cells
that fire together, wire together"
Hebb's rule "cells
that fire together, wire together"Gordon Allport posits additional ideas regarding cell assembly theory and its role in forming engrams, along the lines of the concept of auto-association, described as follows: