some
useful links of thousands
similar
scope of resarch:
Scale-Free Thinking by Eyal Sivan
Tags: barabasi, black swan, cantor, e.o. wilson, eusocial, fractal, gladwell,kelly, leibniz, long tail, mandelbrot, power law, scale-free, superorganism
trackback
In the Mandara Mountains of northern Cameroon live the Mofu,
ethnic tribes whose culture is based on a reverence for social insects.
Their favorite is a breed of ferocious red ant known to them as jaglavak. There are many other species too: ndroa, mananeh and ndakkol.
These names all have one thing in common: they are both plural and
singular. Jaklavak refers equally to one ant, a colony of ants, or all
the ants in the world.
When
we look at an ant colony, we see a group of individual units, but when
the Mofu look at an ant colony, they see a single being. Whether you
zoom in on one ant, or zoom out to see a whole colony, each of these
scales presents a unique and singular entity. The ant and the colony
each has its own properties, behaviours and adaptations. If this view
resonates with you, then you are thinking scale-free.
Scale-Free Mathematics
Imagine
a line of fixed length. Now split that line into thirds and remove the
middle third, leaving you with two lines. Now split each of those into
threes and remove the middles, so that you have four lines. Keep
splitting each line, again and again, to infinity. Now, how long is the
total set of lines and spaces? Still the same original fixed length, of
course. But how many smaller lines and spaces is it made up from?
Infinite lines and infinite spaces. So is this new shape of fixed
length or infinite length? That is exactly the thought experiment
introduced by German mathematician Georg Cantor in 1883 when he defined the Cantor set:

The
unique thing about a Cantor set is its simplicity. Taking the result of
a very simple process and feeding it back into itself over and over, ad
infinitum, results in a highly complex shape. This process, known as recursion,
creates a shape where no matter how far you zoom in, it always looks
the same as where you started. At any magnification, the parts are
similar to the whole. In mathematics, this property came to be called self-similarity, and it marks the dawn of formal scale-free thinking. ...
|
The Self-Organizing Universe is a seminal book by Erich Jantsch that deals with self-organization as a unifying evolutionary paradigm that incorporates ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Self-Organizing_Universe - 1
|
eco devo universe community EDU
The underlying paradigm for cosmology is theoretical physics. The
EDU research community explores how it might be extended by including
insights from evolutionary developmental biology. In the neo-Darwinian
paradigm, adaptive evolutionary development allows the production of
ordered and complex structures. More specifically, we can distinguish evolutionary processes which are contingently adaptive and developmental processes
which produce systemically statistically predictable structures and
megatrajectories internal to the developmental cycle. By analogy with
the evolutionary development of two genetically identical twins, would
two initially parametrically identical universes each exhibit
unpredictably separate and unique evolutionary differentiation over
their lifespan, and at the same time, a broad set of predictable
developmental milestones and shared structure and function between
them? More generally, can we model our universe as an evolutionary
developmental system?
John Smart
EvoDevoUniverse ?
A Framework for Speculations on Cosmic Culture
in Cosmos and Culture, Steven J. Dick (ed.), NASA
Press (forthcoming).
Abstract evodevouniverse
The
underlying paradigm for cosmology is theoretical physics. In this paper
we explore ways this framework might be extended with insights from
information and computation studies and evolutionary developmental
(evo-devo) biology. We also briefly consider implications of such a
framework for cosmic culture. In organic systems, adaptive evolutionary
development guides the production of intelligent, ordered and complex
structures. In such systems we can distinguish evolutionary processes
which are chaotic, creative, and contingently adaptive, and
developmental processes which produce convergent, conservative, and
systemically statistically predictable structures and trajectories.
By
analogy with two genetically identical twins, would two parametrically
identical universes each engage in unpredictably different and unique
evolutionary pathways over their lifespan, and at the same time, share
a broad set of predictable developmental milestones, structure and
function between them? We suggest so.
We will briefly model our
universe as an informational, evolutionary and developmental system−as
an info evo devo universe (abbreviated ‘evo devo universe’ hereafter).
Our framework will try to reconcile the majority of apparently
unpredictable, evolutionary features of universal emergence with a
special subset of statistically predictable and apparently
developmental universal trends, including:
• accelerating emergences (significant advances), in universal complexity, a pattern seen over the last half—but not the first half—of the universe’s history
• increasing spatial and temporal locality of universal complexity development
•
apparently hierarchical emergence of increasingly matter- and
energy-dense, and matter- and energy-efficient ‘substrates’ (platforms)
for adaptation and computation
• the
apparent accelerating trend, on Earth, toward increasingly
postbiological (technological) systems of physical transformation and
computation.
Hypercycle and the Operator Hierarchy
Gerard Jager's Website gives a detailed overview describing the ingredients of his Operator Hierarchy.
The basic concept is a recurrent evolution of operators in nature from
superstrings to biological memons going through distinct phases of
closure.:
superstring, hadron, atom, cell, memon (multicellular entity with neural network).
The Santa Fe Institute
is devoted to creating a new kind of scientific research community, one
emphasizing multi-disciplinary collaboration in pursuit of ...
www.santafe.edu/
Geoffry's West research on hierarchical branching network systems can be considered as pathbreaking.
It's a young institute with a very open upstart, but already showing
sings of being institutuionalized into disciplines with
shaded
eyeglasses for truly transdisciplinary research
Vince@santafe.edu
: complex systems and evolution links
spacefilling energy transformation networks
Universal evolution http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolution_(philosophy)
Vernadsky's and Teilhard's theories
Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky and Pierre Teilhard de Chardin
independently formulated very similar theories describing the gradual
development of the Universe from subatomic particles to human society
and beyond. Teilhard's theories are better known in the West (and have
also been commented on by Julian Huxley), and integrate Darwinian evolution and Christianity, whilst Vernadsky wrote more purely from a scientific perspective, and his ideas contributed to Gaia theory.
Three classic levels are described. Cosmogenesis (Teilhard) or the formation of inanimate matter (the Physiosphere of Wilber), culminating in the Lithosphere, Atmosphere, Hydrosphere,
etc (Teilhard), or collectively, the Geosphere (Vernadsky). Here
progress is ruled by structure and mechanical laws, and matter is
primarily of the nature of non-consciousness (Teilhard - the "Without").
This is followed by Biogenesis (Teilhard) and the origin of life or the Biosphere (Vernadsky, Teilhard), where there is a greater degree of complexity and consciousness (Teilhard - the "Within"), ecology ((Vernadsky) comes into play, and progress and development is the result of Darwinian mechanisms of evolution.
Finally there is human evolution and the rise of thought or cognition
(Vernadsky, Teilhard), and a further leap in complexity and the
interior life or consciousness (Teilhard), resulting in the birth of
the Noosphere
(Vernadsky, Teilhard). Just as the biosphere transformed the geosphere,
so the noosphere (human intervention) transformed the biosphere
((Vernadsky). Here the evolution of human society (socialization) is
ruled by psychological, economic, informational and communicative
processes.
For Teilhard there is a further stage, one of spiritual evolution, the Christing of the collective noosphere, in which humanity converges in a single divinisation he calls the Omega Point.
Natural
Genesis
an
excellent synopsis of the present day state of the art,
the outlook however seems to me
"new age" oriented
 |
The universe is progressing in
a direction
toward greater intelligence, conscious awareness, &
self-understanding. The dark universe becomes gradually more lit up
with consciousness.
David Grinspoon
|
 |
This sourcebook documents the rising
planetary
vision of an organically developing universe, a cosmic genesis, by way
of an annotated bibliography and anthology with over 1500
entries.
Instead of an alphabetic list, its outline conveys this once and future
narrative of a quickening, numinous creation which involves human
participation. Of special note will be a respectful accord
with prior
wisdom and how it might advise a better, more tolerant, sustainable
future.
Cosmic Evolution
An excellent site illustrating the evolution from the big bang to present day humanity and future
Cosmic evolution is the scientific study of universal change. It is an intellectual framework that offers a grand synthesis of the many varied changes in the assembly and composition of radiation, matter, and life throughout the history of the universe.
While engaging the time-honored queries of who we are and whence we
came, this interdisciplinary subject attempts to unify the sciences
within the entirety of natural history—a single broad scientific narrative of a possible origin and evolution of all material things, from an inferred big bang to humankind. (Closely related subjects include epic of evolution, big history, and astrobiology).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cosmic_evolution
the physicist Laurent Nottale, who developped a scale-relativity
theory, to explore the fractal dimension of space-time. He also applied
some of these principle to evolution. See http://luth2.obspm.fr/~luthier/nottale/ukrechel.htm for more infos.
Eric Chaisson, cosmologist and system theorist, who developed a quantitative measure for complex systems. See http://www.tufts.edu/as/wright_center/eric/ericrsrch.html
James Grier Miller (1978) wrote
a 1102-page volume to present his living systems theory.
He constructed a general theory of living
systems by focusing on ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Living_systems_theory
- 34k -``
note: the giant book still fills a central place in my very
special systems library. It should be on the bookshelf of any serious
systems scientist (if he has still books on his shelf).
The
director of the ISCS is Peter A. Corning,
Ph.D., who is known especially for his work on the causal role of synergy
in evolution, most notably in his ...
www.complexsystems.org/ - 8k -r |
Center
for the Study of complex systems CSCS
CSCS university of Michigan
The Center supports the efforts of interdisciplinary groups of
researchers that take a complex systems approach to the phenomena they
study. These groups are composed of University of Michigan faculty
(Primary CSCS Faculty and Associated CSCS Faculty), researchers and
students. CSCS also has a number of active research partnerships with
organizations such as the Santa Fe Institute, Ford Research
Laboratories and Argonne National Laboratory, among others.
Research Groups and
Projects
A list of CSCS research groups, both active and inactive, with links
to further information.
Computational
Biology collaboratiorium
the central hub of a collaborative network of
research institutions
Progress in life sciences is increasingly dependent on research and
development in Computational Biology. In recent years, this research
area
underwent major growth at an international scale not hitherto
paralleled in
Portugal. Because biotechnology is an inherently interdisciplinary
field, it is
notoriously dependent on networks of collaboration (Powell et al 1996).
Indeed,
most researchers involved in new inventions in biotechnology can be
linked via a
network of scientific collaboration (Fleming, 2004). As biotechnology
increasingly adopts an open-science paradigm, successful research
depends not
only on individual know-how, but also on collective know-whom.
Group
of Complex Systems & Random Networks
University of Aveiro, Portugal
Non-equilibrium dynamical systems, Self-organized critically,
Epitaxial Growth, Granular Media,
Small World & Random Networks ....
they are on the right track
Virtual
Knowledge Studio
Physics and Evulution seminar, Bad Honnef, Germany, Jannuary 2008
The Evolution of CitationWebs
modelled by Neural Networks
contribution by Peter Winiwarter related to the emerging field of scientometrics and journalometrics
www.staff.ncl.ac.uk/peter.andras/evcxsysi.htm
www.complexity.org.au/ci/vol02/dgg94/dgg94.html
Systems
Theory and Cybernetics
System
Theory, GST Wikipedia
Systems theory is an interdisciplinary field
of science. It studies the nature of complex systems in nature,
society,
and science.
More specificially, it is a framework by which one can analyze and/or
describe any group of objects that work in concert to produce some
result. This could be a single organism, any organization or society,
or any electro-mechanical or informational artifact.
Highly recommended
reading and site below:
Cybernetics and Systems Science (also: "(General) Systems Theory" or
"Systems Research") constitute a somewhat fuzzily defined academic domain,
that touches virtually all traditional disciplines, from mathematics,
technology and biology to philosophy and the social sciences. It is
more specifically related
to the recently developing "sciences of complexity",
including AI, neural networks, dynamical systems, chaos, and complex
adaptive systems. Its history
dates back to the 1940's and 1950's when thinkers
such as Wiener, von Bertalanffy, Ashby and von Foerster founded the
domain through a series of interdisciplinary meetings.
W. Ross
ASHBY "Introduction to Cybernetics"
The Author of "Design for a Brain" wrote :
"Every
Good Regulator of a System must be a model of that System"
in Int. J. Systems Sci., 1970. vol
1, No. 2 pp89-97
Lotka (the guy from Lotka-Voltera equations) said,
"The principle of natural selection reveals itself as capable of
yielding information which the first and second laws of thermodynamics
are not competent to furnish. The two fundamental laws of
thermodynamics are, of course, insufficient to determine the course of
events in a physical system. They tell us
that certain things cannot
happen, but they do not tell us what does happen."
Howars Odum
is on the right track:
Self-organization
& Networks:
Self-organization
is a process of attraction and repulsion in which the internal ...
between emergence and self-organization
remains an active research ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-organization
-
Complex adaptive systems are special cases of
complex systems. They are
complex
in that they are diverse and made up of multiple interconnected
elements and
adaptive in that they have the
capacity to change and learn from experience. The term
complex
adaptive systems (CAS) was coined at the interdisciplinary
Santa Fe Institute
(SFI), by
John H. Holland,
Murray Gell-Mann and
others.
A Complex Adaptive System (CAS) is a dynamic network of many agents
(which may represent cells, species, individuals, firms, nations)
acting in parallel, constantly acting and reacting to what the other
agents are doing. The control of a CAS tends to be highly dispersed and
decentralized. If there is to be any coherent behavior in the system,
it has to arise from competition and cooperation among the agents
themselves. The overall behavior of the system is the result of a huge
number of decisions made every moment by many individual agents.
Hypercycles
and Evolution
Manfred Eigen and Peter Schuster, "The Hypercycle;
principles of Natural Self-Organization",
Springer, Berlin 1979, page 86
Evolution
of Complex Systems. 1 Table of Contents; 2 Motivation. 2.1
Challenges; 2.2 Hierarchical Life Units (Symbiotic Hierarchical Evolution)
...
www.geocities.com/ResearchTriangle/1402/EvolutionOfComplexSystems.htm
|
Self-organization
is a process where the organization (constraint,
redundancy) ... Self-organization
and complexity in the natural sciences ...
pespmc1.vub.ac.be/SELFORG.html
-
Thus self-organization,
which I find to be one of the most ... Self-organization
is not just something I find interesting, it's also my research topic. ...
cscs.umich.edu/~crshalizi/notebooks/self-organization.html
... I sketch a rough
taxonomy of self-organization
which may be of relevance in the ... on the one
hand, that self-organization
alone is not rich enough for ...
informatics.indiana.edu/rocha/ises.html
-
Nonlinear
Dynamics and Complex Systems Theory
A very exhaustive
glossary of the
terminology in the field of "self-organization"
If you want to talk "self-organization" here are all the buzzwords for
experts in this field.
Bibliography on the Dynamics of complex Systems and Self-organization
vere exhaustive bibliography of books in english and french, chapterheadings in French
self-organization
and artificial life
To
What Extent is War a Self-Organized Emergent Dynamical Process?
To
What Extent is War a Self-Organized Emergent Dynamical P
-
Self Organization
in Space and Lab Plasmas. Some intriguing questions... (5) Self
organization and emergence: There are at least
two paradigms for the ...
plasma.physics.swarthmore.edu/selforg/index.html
-
13k
-
... vague, it is
because the term "self-organization"
has been used in a variety of ... organization
is stabilized, it should possibly be useful to speak of ...
www.imprint.co.uk/thesaurus/self_organization.htm
-
11
Self-organization,
Entropy and Extropy
Many people will have heard of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. That's
the one that states that
the Universe is forever running down towards a "Heat Death". It is
based on the concept of Entropy.
This has several definitions - the inability of a system to do work; a
measure of the disorder in a system
and the one most often used nowadays - the tendency of a system to
enter a more probable state,
usually described as being to create chaos from order. Here we will
look at the opposite idea,
that order and not chaos
is the most probable state.
self-organization
an inherent necessity of nature?
Something is self-organizing if, left to itself, it tends
to become more
organized. This is an unusual, indeed quite counter-intuitive property:
we
expect that, left to themselves, things get messy, and that when we
encounter a
very high degree of order, or an increase in order, something, someone,
or at
least some peculiar thing, is responsible. (This is the heart of the
Argument
from Design.) But we now know of many instances where this expectation
is
simply wrong, of things which can start in a highly random state and,
without
being shaped from the outside, become more and more organized. Thus
self-organization, which I find to be one of the most interesting
concepts in
modern science --- if also one of the most nebulous, because the ideas
of
organization, pattern, order and so forth are, as used normally, quite
vague.
Evolution
of Networks
S.N.
Dorogovtsev, J.F.F.
Mendes
(Submitted on 7 Jun 2001 (
v1),
last revised 7 Sep 2001 (this version, v2))
Abstract:
We review the recent fast progress in statistical physics of evolving
networks. Interest has focused mainly on the structural properties of
random
complex networks in communications, biology, social sciences and
economics. A
number of giant artificial networks of such a kind came into existence
recently. This opens a wide field for the study of their topology,
evolution,
and complex processes occurring in them. Such networks possess a rich
set of
scaling properties. A number of
them are scale-free and show striking
resilience against random breakdowns. In spite of large
sizes of these
networks, the distances between most their vertices are short -- a
feature
known as the ``small-world''
effect. We discuss how growing networks
self-organize into scale-free structures and the role of the mechanism
of
preferential linking. We consider the topological and structural
properties of
evolving networks, and percolation in these networks. We present a
number of
models demonstrating the main features of evolving networks and discuss
current
approaches for their simulation and analytical study. Applications of
the
general results to particular networks in Nature are discussed. We
demonstrate
the generic connections of the network growth processes with the
general
problems of non-equilibrium physics, econophysics, evolutionary
biology, etc.
Evolution of Networks: From Biological
Nets to the Internet and Www (Relié)
de Serguei
N. Dorogovtsev (Auteur), Jose
Fernando Ferreira Mendes (Auteur), S.
N. Dorogovtsev (Auteur)
"The first natural questions to ask about a network are: What does it
look like? ..." (plus)
another boy
playing with networks
so we prove that most literature growth models (such as linear growth law, Price's. exponential growth law, Rescher's sliding exponential growth law, ...
www.springerlink.com/index/K187373P45062066.pdf - Pages similaires - À noter |
... all the bibliometric laws known and all their mathematical expressions are ... Bradford and Lotka) as well as the Price's Law of the exponential growth ...
cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=16801830
Evolution
and Extremum principles
(Minimize dissipated energy
and/or Maximize energy flow)
rediscovery of Zipf's "principle of least effort"
Visual example:
Geese, ducks, swans, cranes and other
birds flye in a V-shaped or oblique line formation in order
to minimize the engergy consumption effort to fly.
(Swimming spermatozoon and ondulatory swimming microorganisms do
likewise.)
"Biophysics", Springer Verlag, Berlin 1983, page 607.
Energetics:
Howard T. Odum 4 laws of energetics - Wikipdia
He is known for his pioneering work on ecosystem ecology
together with his brother Eugene Odum,
but also for his provocative proposals for additional laws of
thermodynamics, proposals which were informed by his work within general systems theory.
Hierarchical
branching Energy transformation Networks
Geoffrey West (president Santa Fe Institute):
"Organisms have evolved to
i) Minimize energy
dissipated in the network.
and / or
ii) Maximize the scaling of their area of interface with their resource
environment."
Co-evolution
:
-
[ Traduire cette page ]
In
biology, co-evolution
is the mutual evolutionary influence between two species. Each party in
a co-evolutionary relationship exerts selective pressures ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Co-evolution
- 27k |
cosmic co-evolution
In cosmic evolution,
ontogeny is regulated by the interplay of physical forces and the results,
both in the macro- and the microbranch of
co-evolution, are passed on in the form of matter. Whereas macroevolution,
in this phase, is at first characterized primarily by the condensation
of matter, and therefore by conservative self-organization, different processes
play a role in the synthesis of matter in microevolution; they also result
in equilibrium structures (stable nuclei and atoms)
- or it seems so at least from a macroscopic or intermediate angle of view.
The increasingly active co-evolution of both branches seems to bring dissipative
self-organization of macrostructures - cores of galaxies and stars - into play. Ontogeny dominates in cosmic evolution. However, there is a kind of unordered "phylogeny" in which matter is transferred criss-cross to new evolutionary sequences. As in the later biological phylogeny, complexity
is thereby furthered; here in the form of planetary systems. Also, a controlled
long-time burning of smaller stars, such as our sun, is ensured by the
carbon cycle which depends on the "phylogeny" of some carbon. This controlled
burning, in turn, makes the development of biological complexity on our
planet possible. The units of this early phylogeny are highly normalized.
The particularities of the history of matter transferred in such a way
may be reconstructed only in vague contours, primarily by isotopic ratios
which, for example, permit the exact dating of a nearby supernova explosion.
In this way, we have only recently discovered something about the supernova
which acted as a midwife for our solar
system.
 Erich Jantsch, The Self-Organizing Universe - Scientific and Human Implications of the Emerging Paradigm of Evolution, New York: Pergamon. 1980, pp.208-209
Erich Jantsch, The Self-Organizing Universe - Scientific and Human Implications of the Emerging Paradigm of Evolution, New York: Pergamon. 1980, pp.208-209

The Nature of Evolution
Alexander Laszlo
a synopsys of the concepts of evolution to be published in World Futures
First
some definitions: coevolution is a change in the
genetic composition of one species (or group) in response to a genetic
change in another. ...
biomed.brown.edu/Courses/BIO48/27.Coevolution.HTML
- 11k |
The Coevolution
Institute's (CoE) mission is to catalyze stewardship of biodiversity.
Since its inception in 1997 as a 501 (c)(3) not-for-profit corporation ...
www.coevolution.org/
- 10k |
Co-evolution
in Epistemic Networks
gents producing and exchanging knowledge are forming as a whole a
socio-semantic complex system. Studying such knowledge communities
offers theoretical challenges, with the perspective of naturalizing
further social sciences, as well as practical challenges, with
potential applications enabling agents to know the dynamics of the
system they are participating in.
The present thesis lies within
the framework of this research program. Alongside and more broadly, we
address the question of reconstruction in social science.
Reconstruction is a reverse problem consisting of two issues:
(i)
deduce a given high-level observation for a considered system from
low-level phenomena; and
(ii) reconstruct the evolution of high-level
observations from the dynamics of lower-level objects.
The lake Constance Case study.
Characterization of an ecosystem in transition
http://www.schweizerbart.de/pubs/isbn/es/archivadva-3510470559-desc.html
Pareto
Zipf Mandelbrot PZM power laws :
the same thing
over and over again, rediscovered by virtually every
compartment of reductionist science.
Power laws, Pareto distribution and Zipf's law
V. CONCLUSIONS
In this review I have discussed the power-law statistical
distributions seen in a wide variety of natural and
man-made phenomena, from earthquakes and solar flares
to populations of cities and sales of books. We have seen
many examples of power-law distributions in real data
and seen how to analyse those data to understand the behaviour
and parameters of the distributions. I have also
described a number of physical mechanisms that have
been proposed to explain the occurrence of power laws.
Perhaps the two most important of these are:
1. The Yule process, a rich-get-richer mechanism in
which the most populous cities or best-selling books
get more inhabitants or sales in proportion to the
number they already have. Yule and later Simon
showed mathematically that this mechanism produces
what is now called the Yule distribution,
which follows a power law in its tail.
2. Critical phenomena and the associated concept of
self-organized criticality, in which a scale-factor of a
system diverges, either because we have tuned the
system to a special critical point in its parameter
space or because the system automatically drives itself
to that point by some dynamical process. The
divergence can leave the system with no appropriate
scale factor to set the size of some measured
quantity and as we have seen the quantity must
then follow a power law.
The study of power-law distributions is an area in
which there is considerable current research interest.
While the mechanisms and explanations presented here
certainly offer some insight, there is much work to be
done both experimentally and theoretically before we can
say we really understand the physical processes driving
these systems. Without doubt there are many exciting
discoveries still waiting to be made.
Relation to Zipf's law.
Pareto distributions are continuous probability ....
Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the
Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pareto_distribution
- 65k
Zipf's law states that
given
some corpus of natural language utterances, ....
Comprehensive bibliography of Zipf's law
· Zipf, Power-laws,
and Pareto - a ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zipf's_law
- 54k
|
Ruiz-Banos R; Bailon-Moreno R; Jimenez-Contreras E; Courtial JP Structure and dynamics of scientific networks. Part II: The new Zipf's Law, the clusters of ...
www.garfield.library.upenn.edu/histcomp/scientometrics/index-au1-17.html - 54k
|
Abstract Here,
the quantitative theory of translation is shown to be of great utility
in describing scientific networks. In fact, we deduce a new Zipf's Law
for the descriptors of a set of documents, based on the concepts of
centres of interest and of irreversible parallel translations. This new
law can be generalized to other phenomena, such as the distribution of
the sizes of cocitation clusters. Finally, we have established the
model, for descriptor presence in a network, which closely fits the
values recorded.
Zipf-Mandelbrot
law, Wikipedia
In probability theory and statistics, the Zipf-Mandelbrot
law is a discrete probability distribution.
Also known as the Pareto-Zipf law, it is a power-law
distribution on ranked data,
named after the Harvard linguistics professor
George Kingsley Zipf (1902-1950)
who suggested a simpler distribution called Zipf's law, and the mathematician Benoît Mandelbrot
(born November 20, 1924),
who subsequently generalized it.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zipf-Mandelbrot_law
Pareto Zipf Power laws
Zipf, Power-laws, and Pareto - a ranking tutorial
describes the equivalence of Zipf's law and Pareto law
| Many man made and naturally occurring
phenomena, including city sizes, incomes, word frequencies, and
earthquake magnitudes, are distributed according to a power-law
distribution. A power-law implies that small occurrences are extremely
common, whereas large instances are extremely rare. This regularity or
'law' is sometimes also referred to as Zipf and sometimes Pareto. To
add to the confusion, the laws alternately refer to ranked and unranked
distributions. Here we show that all three terms, Zipf, power-law, and
Pareto, can refer to the same thing, and how to easily move from the
ranked to the unranked distributions and relate their exponents. |
- [ Traduire cette page ]
|
Example of a Pareto frontier. The boxed points represent feasible ... Given a set of choices and a way of valuing them, the Pareto frontier or Pareto set is ...
|
- [ Traduire cette page ]
|
(3) An outcome Oi is Pareto optimal just in case no other possible outcome is Pareto superior to it. (4) The Pareto frontier is the set of all of the ...
|
- [ Traduire cette page ]
|
Tre use of evolutionary algorithms. of this paper is to introduce a novel Pareto frontier Differential Evolution PDE algorithm to solve MOPs.
|
MOP algorithm forces the choice of the first direction, .... Fig. 6. Delay vs. distance for the MOP algorithm in a CSD constellation. ...
Power-law distributions in empirical data
Aaron Clauset,1, 2 Cosma Rohilla Shalizi,3 and M. E. J. Newman4
1Santa Fe Institute, 1399 Hyde Park Road, Santa Fe, NM 87501, USA
2Department of Computer Science, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131, USA
3Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA
4Department of Physics and Center for the Study of Complex Systems, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109,
USA
Power-law distributions occur in many situations of scientific interest and have significant consequences
for our understanding of natural and man-made phenomena. Unfortunately, the empirical
detection and characterization of power laws is made difficult by the large fluctuations that occur
in the tail of the distribution. In particular, standard methods such as least-squares fitting are
known to produce systematically biased estimates of parameters for power-law distributions and
should not be used in most circumstances. Here we describe statistical techniques for making
accurate parameter estimates for power-law data, based on maximum likelihood methods and the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic. We also show how to tell whether the data follow a power-law distribution
at all, defining quantitative measures that indicate when the power law is a reasonable
fit to the data and when it is not. We demonstrate these methods by applying them to twentyfour
real-world data sets from a range of different disciplines. Each of the data sets has been
conjectured previously to follow a power-law distribution. In some cases we find these conjectures
to be consistent with the data while in others the power law is ruled out.
Format de
fichier: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Version
HTML
Recall the 2nd Zipf’s law
for. the number of words of given. frequency:. n(f) ∼ f ...
scale-free (Barabasi, Albert’99), internet
P(k) ∼ k ...
www.lpm.u-nancy.fr/webperso/chatelain.c/GrpPhysStat/PDF/Yu_nancy07a.pdf
-
In
seismology, the Gutenberg-Richter law
expresses the relationship between the magnitude and total number of
earthquakes in any given region and time ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gutenberg-Richter_law
- 16k
Lotka's law [1], named
after Alfred J. Lotka, is one of a variety of special applications of
Zipf's law. It describes the frequency of
publication by ...
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lotka's_law
- 19k
Maximum
Power Principle, Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maximum_power_principle
The maximum power principle
has been proposed as the fourth principle of energetics
in open system thermodynamics, where an
example of an open system is a biological cell.
Bradford's
law, Wikipedia
Bradford's law
is a pattern first described by Samuel C.
Bradford in 1934 that estimates the exponentially diminishing returns of
extending a search for references in science journals.
These papers may be about "Pareto's
principle", "Lotka's law", "Bradford's law",
"Benford's law", "Heaps' law",
etc, or may be about power-law
in general. ...
www.nslij-genetics.org/wli/zipf
Format de
fichier: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Version
HTML
power-law behaviour. In economics
prime examples are the distributions of incomes (Pareto’s.
law) and city sizes (Zipf’s
law or the rank-size property), ...
linkage.rockefeller.edu/wli/zipf/reed01_el.pdf
Format de
fichier: PDF/Adobe Acrobat - Version
HTML
Power laws, Pareto distributions
and Zipf’s law. Many
of the things that scientists measure have a typ-. ical size or
“scale”—a typical value around which ...
www-personal.umich.edu/~mejn/courses/2006/cmplxsys899/powerlaws.pdf
-
Generalized
Lotka Volterra GLV
http://ideas.repec.org/p/sce/scecf1/11.html
Generalized Lotka-Volterra (GLV) models
extending the (70 year old)
logistic equation to stochastic systems consisting of a multitude of
competing auto-catalytic components lead to power distribution laws of
the (100 year old) Pareto-Zipf type. In particular, when applied to
economic systems, GLV leads to power laws in the relative individual
wealth distribution and in the market returns. These power laws and
their exponent a are invariant to arbitrary variations in the total
wealth of the system and to other endogenous and exogenous factors. The
measured value of the exponent a = 1.4 is related to built-in human
social and biological constraints.
G/A, [] R. Kohli and R. Sah, Market
shares:Some power
law results and .... Punctuated
equilibrium and criticality in a simple model of evolution.
Phys. Rev. ...
www.citebase.org/abstract?identifier=oai%3AarXiv.org%3Acond-mat%2F0412004&action=citeshits&citesh...
- 60k
The
reason we care about power law
correlations is that we're conditioned to think ....
M. E. J. Newman, "Power laws, Pareto
distributions and Zipf's law", ...
www.cscs.umich.edu/~crshalizi/notebooks/power-laws.html
- 34k
etc ...
auto-catalytic elements posses power
law distributions of the Pareto-Zipf
type. ... n - Ecology and evolution.
89.75.Da - Systems obeying scaling laws. ...
www.edpsciences.org/articles/epjb/abs/2002/10/b02128/b02128.html
-
We investigate a model of evolving random network,
introduced by us
previously [ıt Phys. Rev. Lett. bf 83, 5587 (1999)] . The model is a
generalization of the Bak-Sneppen model of biological evolution, with
the
modification that the underlying network can evolve by adding and
removing
sites. The b ...
Comment: 9 pages, 11 figures, submitted to Phys. Rev. E (substantially
revised version)
Zipf and Pareto-like
plots will be given. After deducing empirical laws, ...
1(b), it can be seen that the Pareto distribution
roughly follows a power law ...
stacks.iop.org/0295-5075/77/i=3/a=38002/html
Y.Choi and H.Kim
Physica A.
382/665, 2007.
Entry listings in a dictionary of mythic provenance can
be seen as
nodes
in a scale-free, power-law array similar to complex
systems found
throughout biological, social, economic, and internet
domains. Whatever universality might human inquiry and
narrative lately
be able to realize?
- [ Traduire cette page ]
|
The Mathematical Theory of Infectious Diseases and its Applications 2nd Ed. Charles Griffin, ..... Power laws, pareto distributions and Zipf's law. Contemp. ...
portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1132952.1132954
|
- [ Traduire cette page ]
|
From the *Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases, Emory University School of ..... Power laws, Pareto distributions and Zipf's law. ...
www.stdjournal.com/pt/re/std/fulltext.00007435-200708000-00015.htm;jsessionid=GpyNvqjs5dgMYVjJgZ5gPmcq1JQ...
|
Format de fichier: PDF/Adobe Acrobat -
Version HTML
the stochastic mechanism called the
Zipf-Estroup
law (Estroup, 1916;
Zipf,
..... Mathematical Approaches for Emerging and Reemerging
Infectious Diseases:
...
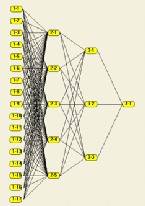
www.csss.washington.edu/Papers/wp31.pdf -
Neural
Networks
Download a free evaluation copy of NeuroSolutions
to discover how to apply neural network technology to your artificial
intelligence application.
www.nd.com/ - 15k
Multidimensional Neural Networks Unified Theory
Rama Murthy, G. Faculty member of the International Institute of Information Technology
http://www.newagepublishers.com/servlet/nagetbiblio?bno=001548
| 158
Designing neural networks using genetic algorithms
with grap. ... 37 Intrinsic adaptation in a simple model
for evolution (context) - Pack |
If a network has more layers and. its inputs are interrelated, more coimplex patterns can be. generated. If the stochastic property of the PLN element ...
Memory, Learning, Intelligence
The Ontogeny of Memory and Learning:
Natural Intelligence versus Artificial Intelligence in
Information Technology Education
Research networks
Complexity
Digest - Networking the Complexity Community
Complexity digest (ComDig)
provides weekly news digest from the fields of science of complexity.
It reproduces abstracts of articles dealing with complex ...
www.comdig.org/ - 78k -
enter PARETO as search
term
- Power
Laws, Pareto
Distributions and Zipf's Law [ 2005.02
]
- Two-Factor
Model of Income Distribution Dynamics [ 2004.48
]
- Power
[ 2007.07
]
- Multiobjectivity
And Complexity In Embodied Cognition [ 2005.37
]
- Market
Ecology etc. in Microscopic Simulation of the LLS Stock Market Model
[ 2000.22
]
- Scaling
Laws and Urban Systems [ 2004.09
]
- Social
Segregation and the Dynamics of Group Inequality [ 2006.09
]
- The
Power Laws, The Science of Success [ 2002.27
]
- The
Mind Of A Child [ 2002.27
]
- Power
Laws of Wealth, Market Order Volumes and Market Returns [ 2001.10
]
enter ZIPF as search term
- Zipf Analysis Of Audio Signals
[ 2004.15
]
- On
the Universality of Rank Distributions of Website Popularity
[ 2004.16
]
- Zipf Distribution of U.S. Firm
Sizes [ 2001.37
]
- Scaling
In Public Transport Networks [ 2005.04
]
- Zipf's Law, Music
Classification, And Aesthetics [ 2005.12
]
- The
Mind Of A Child [ 2002.27
]
Search
Engines in Conceptual Space
Sinequa CS Connect to Knowledge™
Sinequa
is a French software publisher and service provider that specializes in
intelligent access to information: semantic search
and navigation
engine, ...
www.sinequa.com/en-index.html
- |
- [ Traduire cette page ]
|
The Mathematical Theory of Infectious Diseases and its Applications 2nd Ed. Charles Griffin, ..... Power laws, pareto distributions and Zipf's law. Contemp. ...
portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1132952.1132954
|
empirical
World Wide Web distributions :
Here
we show that all three terms, Zipf,
power-law, and Pareto,
can refer to the same .... L.A. Adamic and B.A.
Huberman, 'Zipf’s law
and the Internet', ...
www.hpl.hp.com/research/idl/papers/ranking/ranking.html
- 16k
A number of giant artificial networks of such a kind came into existence recently. This opens a wide field for the study of their topology, evolution, ...
arxiv.org/abs/cond-mat/0106144 - |
EVOLUTION OF NETWORKS. From Biological Nets to the Internet and WWW. SN Dorogovtsev | JFF Mendes. Synopsis · Table of Contents ...
sweet.ua.pt/~f2064/b.html - |
[PDF] Growth dynamics of the World wide Web - all 13 versions »
BA Huberman, LA Adamic - J. Reprod. Fertil, 1993 - hpl.hp.com
... tively crawling the web. The distribution of site sizes for crawls by Alexa and
Infoseek is shown in Fig. 1. Both data sets display a power law over several ...
Cited by 368 - Related Articles - View as HTML - Web Search
Search in power-law networks - all 20 versions »
LA Adamic, RM Lukose, AR Puniyani, BA Huberman - Physical Review E, 2001 - APS
... Furthermore, it has been shown that the Internet backbone has a power-law distribution
with exponent values between 2.15 and 2.2 2 , and web page hyperlinks ...
Cited by 549 - Related Articles - Web Search - BL Direct
[PDF] Zipf’s law and the Internet - all 10 versions »
LA Adamic, BA Huberman - Glottometrics, 2002 - hpl.hp.com
... However, the World Wide Web is anything but fixed ... when one computes an exponentially
weighted mixture of lognormals one obtains a power-law distribution exactly ...
Cited by 104 - Related Articles - View as HTML - Web Search
[PDF] Evolutionary Dynamics of the World Wide Web - all 2 versions »
BA Huberman, LA Adamic - Arxiv preprint cond-mat/9901071, 1999 - arxiv.org
... new sites are created at different times in the unfolding story of the Web. This
leads to the prediction of a universal power law in the distribution of the ...
Cited by 57 - Related Articles - View as HTML - Web Search
The Web's hidden order - all 8 versions »
LA Adamic, BA Huberman - Communications of the ACM, 2001 - portal.acm.org
... In order to explain the power law distribution of site sizes, one needs to consider
two additional factors that determine the growth of the Web: sites appear ...
Cited by 84 - Related Articles - Web Search - BL Direct
Frequency
of occurrence of numbers in the World Wide Web
Here, we obtain the
detailed statistics of numbers in the World Wide Web, finding that
their
distribution is a heavy-tailed dependence which splits in a set of
power-law
ones. ....
Movies
and Actors: mapping the Internet Movie database
|
|
Herr, Bruce
W. Ke, Weimao Hardy,
Elisha Borner, Katy
Indiana University;
analysis
of co-actor network (parallel: the the actor network analysis
of greek and roman mythology)
|
Web
Advertising : Left - Right - Brain
Théorie de la longe traîne
(theory of scale
free web advertising budgets)



 Erich Jantsch, The Self-Organizing Universe - Scientific and Human Implications of the Emerging Paradigm of Evolution, New York: Pergamon. 1980, pp.208-209
Erich Jantsch, The Self-Organizing Universe - Scientific and Human Implications of the Emerging Paradigm of Evolution, New York: Pergamon. 1980, pp.208-209
